Nowadays, people have started sanitizing even their smartphones for the fear of getting infected with the deadly coronavirus. However, if you do not want your digital experience to go haywire, it is equally important to be careful about your online activities that you do with your phone such as apps that you download, transactions that you make, the websites that you visit and the activities that you do there.
Threat actors have started taking advantage of this pandemic to expand their victim base and revenue and for this they have decided to make the mobile devices as a storehouse for Trojans. From fake apps that claim to provide information of the current pandemic situation to apps faking protection measures claiming to protect users from getting infected, we have seen it all. For easily capitalizing on their revenue front, Banking Trojans have become their best bet these days considering the fact that all the transactions are being made online as people do not step out for the fear of getting infected. These Trojans spread by using COVID-19 situation as a ruse.
In this blog, we will be looking at the surge in Android Banking Trojans amidst this pandemic time using which threat actors gain access to confidential information of the users when they transact online.
Web Definition of Banking Trojan
A Banker Trojan is a malicious computer program designed to gain access to confidential information stored or processed through online banking systems. Banker Trojan is a form of Trojan horse and can appear as a legitimate piece of software until it is installed on an electronic device.
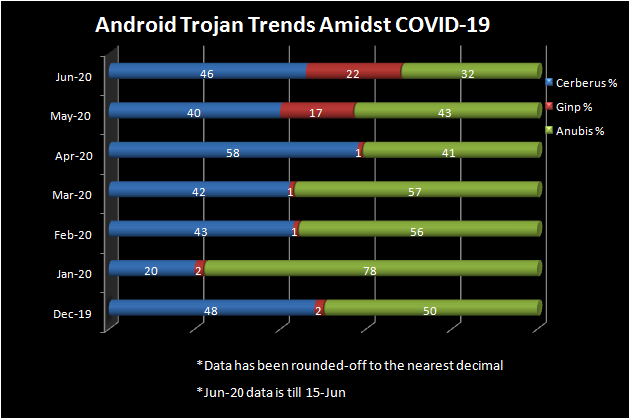
Stats
Stats reveal that there has been a considerable increase in the number of Banking Trojanized apps that have escaped security checks from the official App Store and sneaked their way onto the user’s device. The most infamous few have been Cerberus, Anubis and Ginp. These Trojans try to deceive the users into installing the infected app by faking to give COVID-19 information.
While Cerberus promises to be a “Coronavirus tracker” and uses screen overlay technique to steal credentials and sensitive user data, it also has Remote Access Trojan (RAT) and keylogger functionalities; the Ginp Trojan disguises itself as the app “CoronaFinder” and promises to provide the location information of coronavirus-infected people around the user on the payment of a small amount to steal financially-sensitive information and the Anubis Trojan masquerades itself as a “Coronavirus statistics” app and hides itself to steal the user’s sensitive information.
The chart shows the proportion of malicious banking apps against the total listed for a particular month.
We have tracked these banking malware from Dec-19, the time when COVID-19 was first reported to the World Health Organization (WHO) till mid Jun-20.
We can glean from the statistics depicted above that there has been a steep increase in Banking malware during June, considering the fact that the stats for Jun-20 is only till 15th of June, in comparison to other months.
The proportion of apps affected by Banking Trojans such as Cerberus and Anubis in both Google Play store and third-party markets has shown a considerable increase in Jun-20 when compared to Dec-19, the official confirmation of the start of this deadly pandemic.
This can be attributed to the fact that the threat actors have started taking more and more advantage of the “Work from Home” scenario and the increased use of smartphone based transactions done by users for all necessities, instead of commuting to the needed place. We believe that this trend may continue or even increase further in the coming months and possibly in a post-COVID world.
How do such malicious apps succeed in entering onto a victim’s device and doing its malicious behaviour?
Here are few of the most commonly used techniques amongst many,
- By disabling Google Play Protect
- By disguising themselves as benign apps or using a system name for the app, making it difficult to uninstall
- By hiding the app icon in the launcher
- By posting fake positive reviews of apps by masquerading as the victim and luring users into installing their apps
How are such malicious apps identified?
- Google Bouncer, a Google Security service that verifies an app for its maliciousness or an app with unwanted behaviour even before they are made available in Google Play for users to download
- Google Play Protect protects users from apps that steal data, secretly monitor or harm users, or are otherwise malicious
- Users reporting about malicious app behavior to Google, for removal of those apps
- Nefarious apps being reported by Anti-Virus vendors
With the rise in COVID-19 spread and Android users, developing malware for this mobile OS using COVID-19 as a ploy, has become a profession rather than a hobby for the bad actors. Users are therefore advised to be on guard while downloading seemingly benign apps related to COVID-19 especially and not get deceived by fake reviews posted by threat actors to increase the app rating.
Mitigation Tips
- Keep your devices updated and patched for the latest security vulnerabilities
- Do not click on links in SMS, emails and the like sent to you, especially by unknown senders
- Exercise caution even while installing apps from the official App Store
- Disable “Install unknown apps” on your Android devices. Remember to never download apps from any third-party app store
- Watch out for fake reviews such as checking if a lot of reviews were posted on the same date, reading the reviewer’s profile and also by doing a bit of Googling from your end
- Check app permissions during installation. Abort the process if unnecessary privileges are asked
- Practice good security hygiene
- Scan your device regularly
- Install a robust security product such as K7 Mobile Security to stay protected from the latest threats
We detect all the above listed Banking Trojan variants generically.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
| Trojan Name | Hash | K7 Detection Name |
| Cerberus | fccde7156aa9b25a14ed86985761f7015b813e5021e399750ac14bfcada83808 | Trojan ( 005633ff1 ) |
| Ginp | cdae640237fa190c62f0b1d89e504dc0d728e771026b241b1a549f9c8b6d57c0 | Trojan ( 0055f8ed1 ) |
| Anubis | 70439d393cca65ede64971d923ed61c0dd332dad5e2c31fdf8d225db1cf933e8 | Trojan ( 0053b5f91 ) |