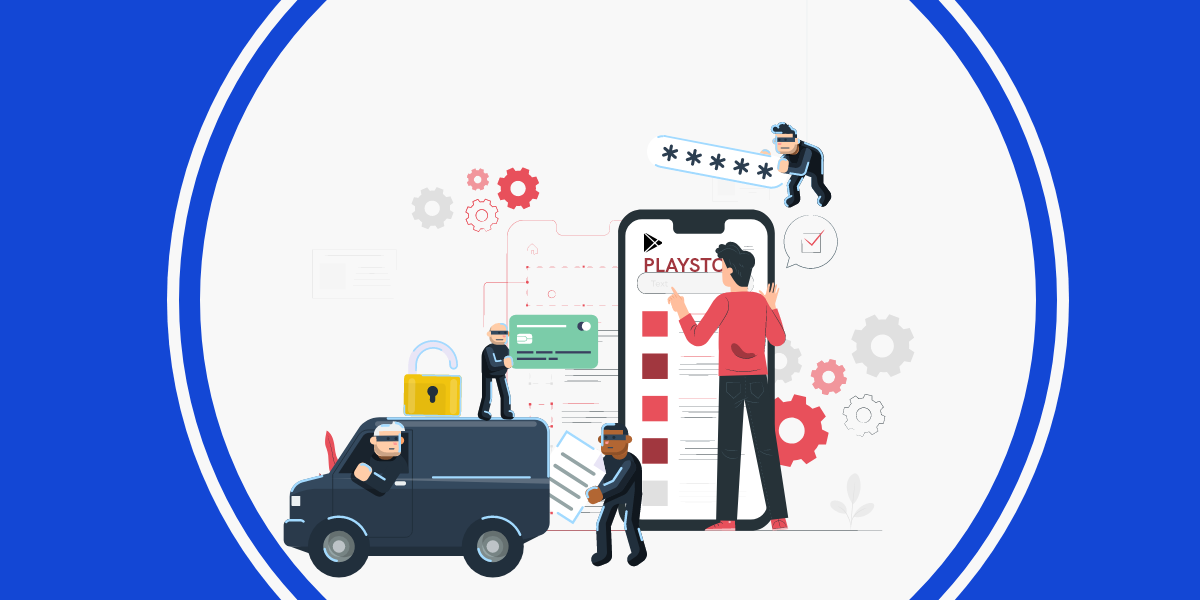
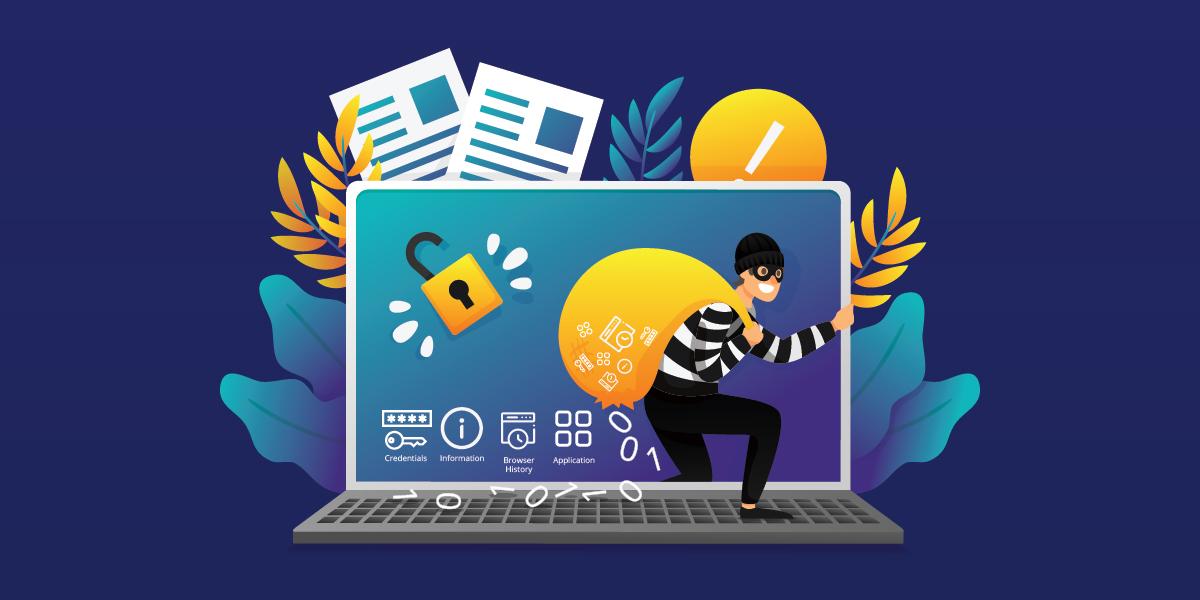
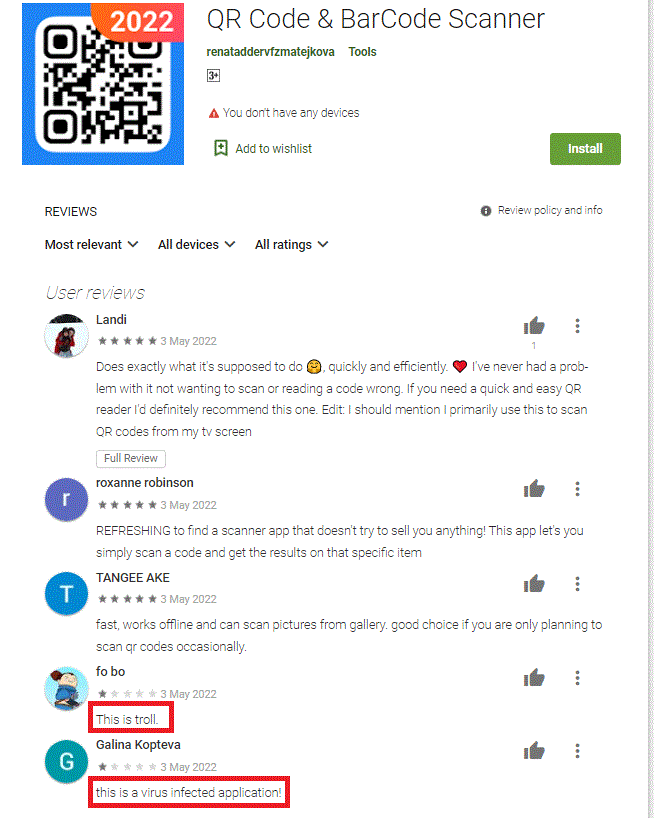
We at K7 Labs recently came across this twitter post aboutTeabot (aka ‘Anatsa’) a banking Trojan. The main infection vector of Teabot was found on the official Google Play Store where it posed as QR Code & BarCode Scanner app with 10,000+ downloads as shown in Figure 1.
Once launched, this app requests the user to update itself via a popup message as shown in Figure 2.
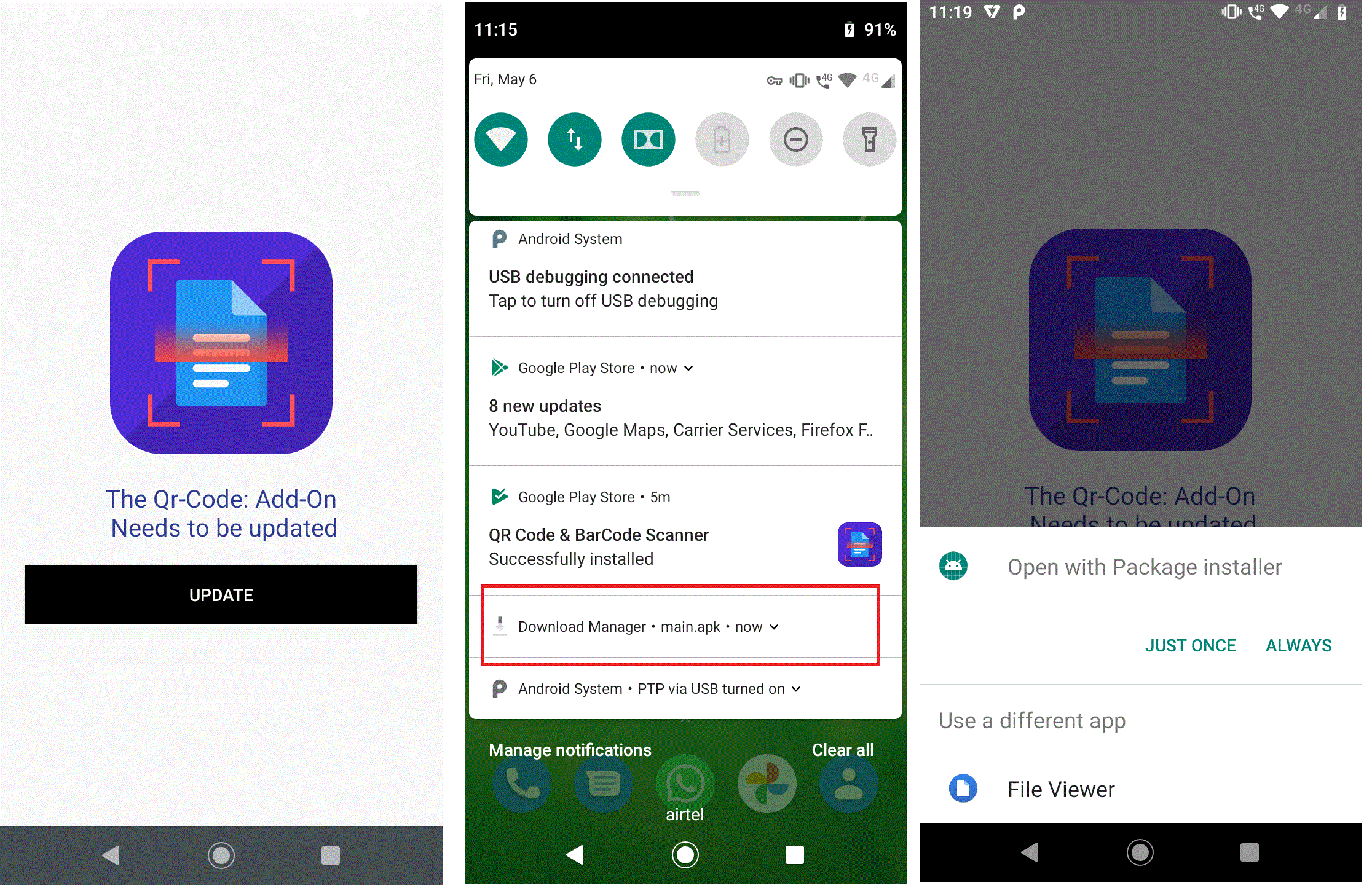
When the user clicks on the “Update” message this application downloads and installs the malicious Teabot Banking Trojan “main.apk” as shown in Figure 2.
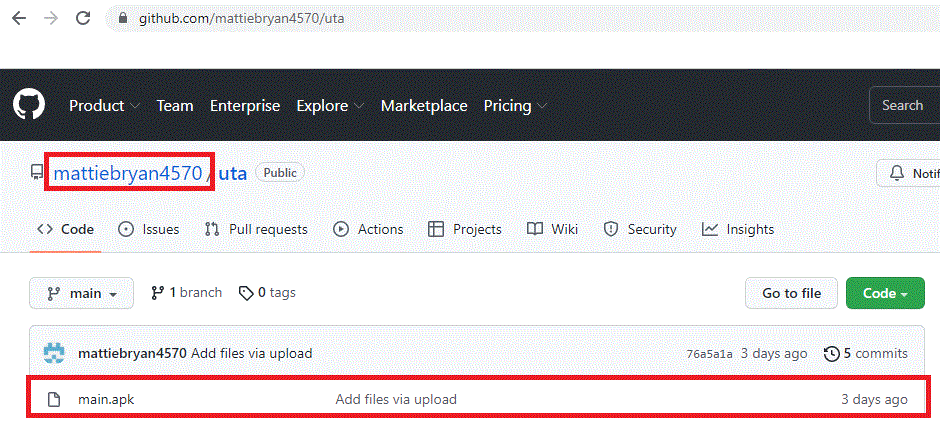
From the ADB Logcat report we noticed that the malware file “main.apk” gets downloaded from a GitHub repository as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 4 shows the repository was created by mattiebryan4570, at the time of writing this blog the GitHub repository was still live.
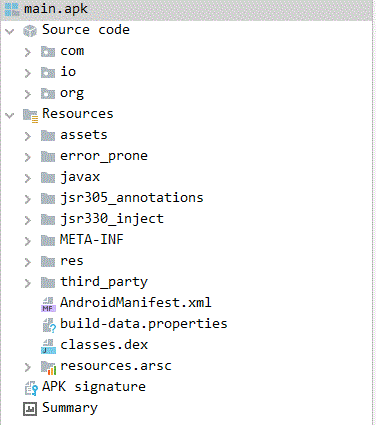
In this blog, we will be analyzing the package “com.joy.slab” corresponding to the main.apk which has been downloaded from the above mentioned GitHub repository as shown in Figure 5.
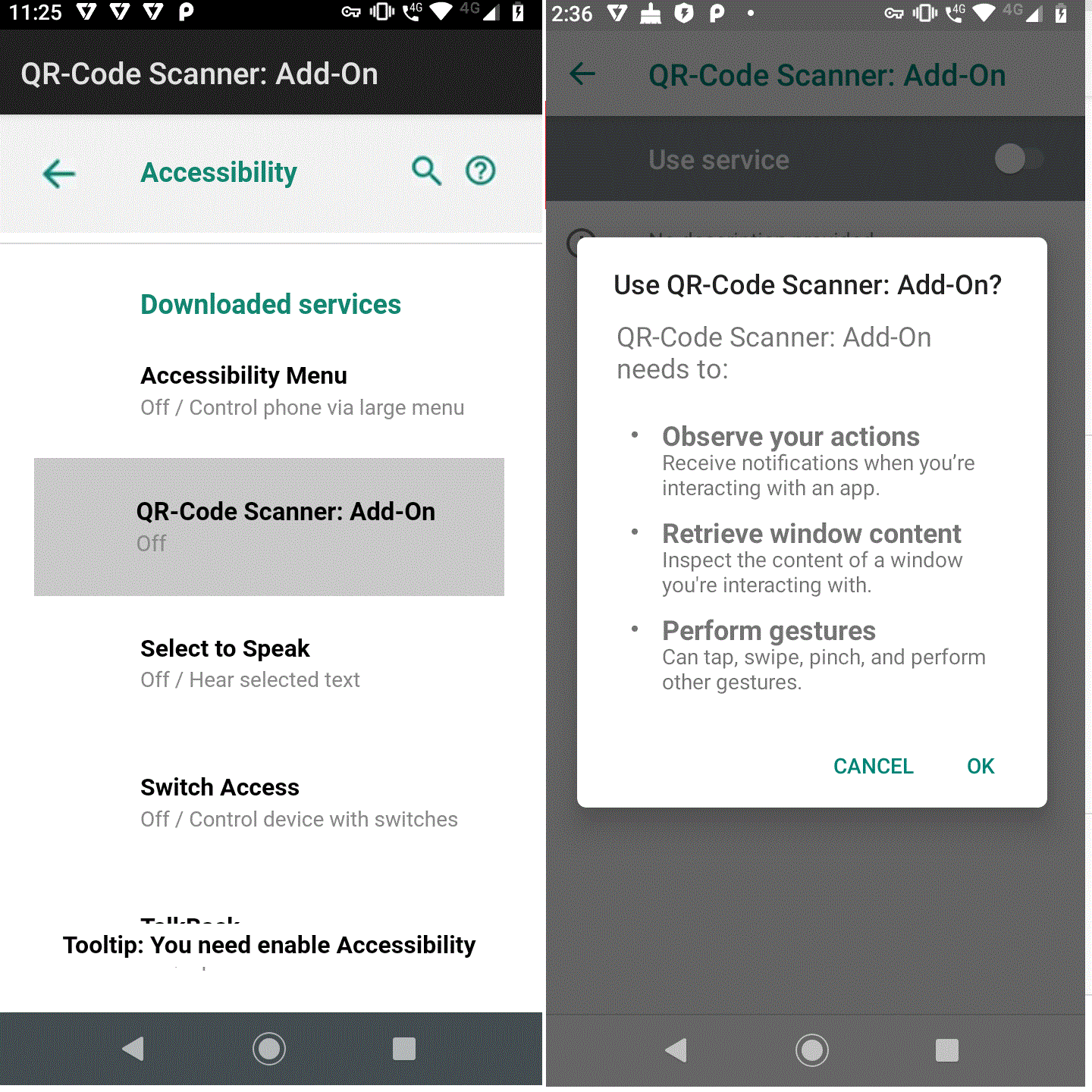
Once the Teabot malware is installed on the device, the app downloads itself as a QR-Code Scanner: Add-On which frequently brings up the Accessibility Service setting option on the device, as shown in Figure 6, until the user allows this app to have the Accessibility Service enabled.
Once the permissions are granted, this malicious apk decrypts the malicious payload file called eepHM.json from the app’s assets folder to an executable dex format named ‘eepHM.odex’ and loads the decrypted file as shown in Figure 7.

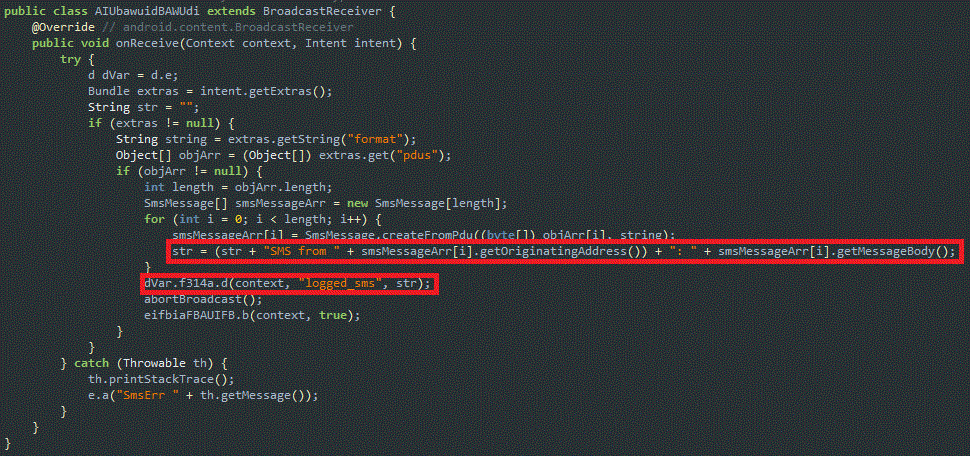
The trojan then attempts to intercept SMS messages and aborts the new SMSReceived broadcast to the victim; as per the bot command “logged_sms” as shown in Figure 8.
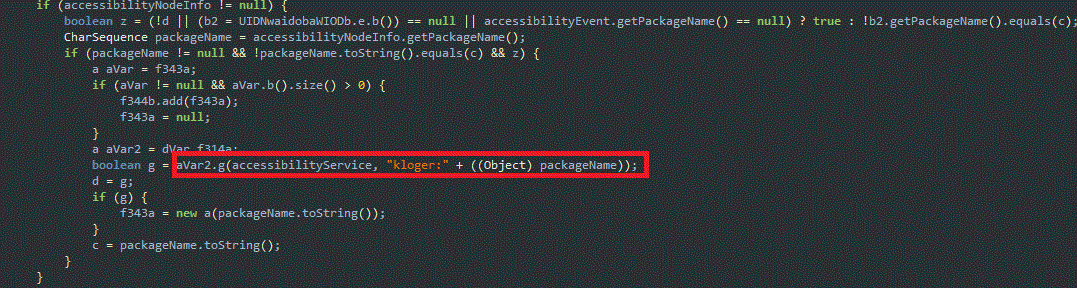
After abusing the Android Accessibility Service, this trojan acts as a keylogger to steal the victim’s keystroke information from the device.
C2 Communication
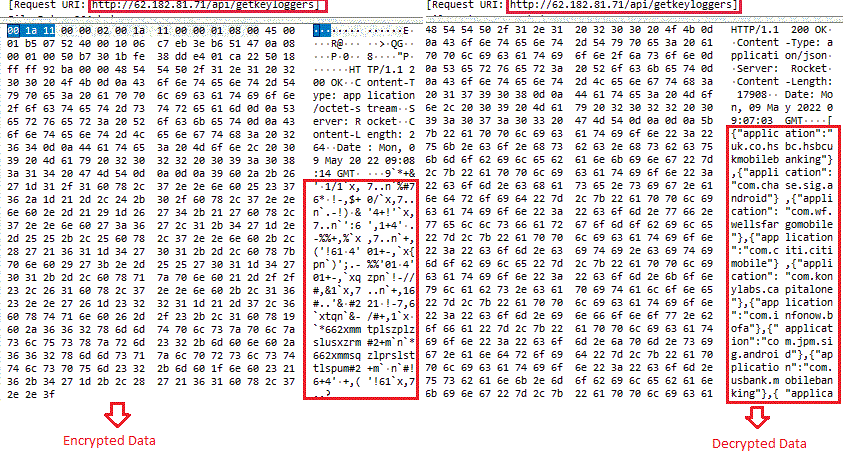
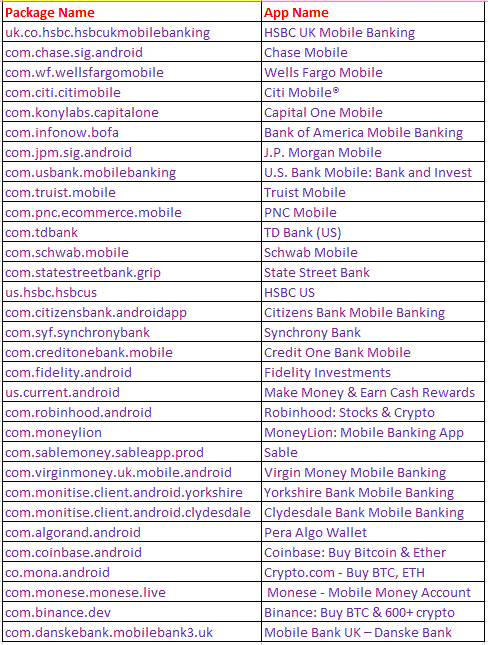
Teabot enumerates the list of installed applications on the victim’s device and then sends this list to the C2 server during its first communication. All the communications between C2 and the malware remain encrypted using an XOR key as shown in Figure 10. When one or more targeted apps are found, the C2 server sends the specific payload(s) to the victim’s device to perform an overlay attack and track all the activity related to the identified targeted application(s).
The following are the targeted applications in a typical victim’s device
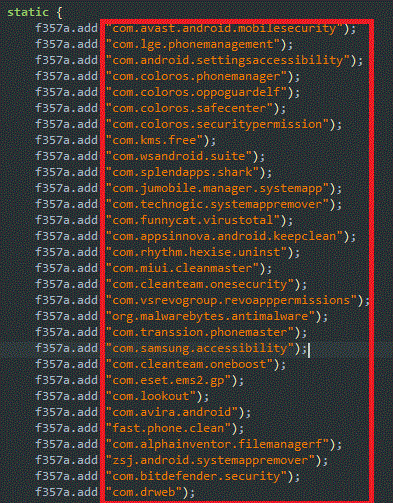
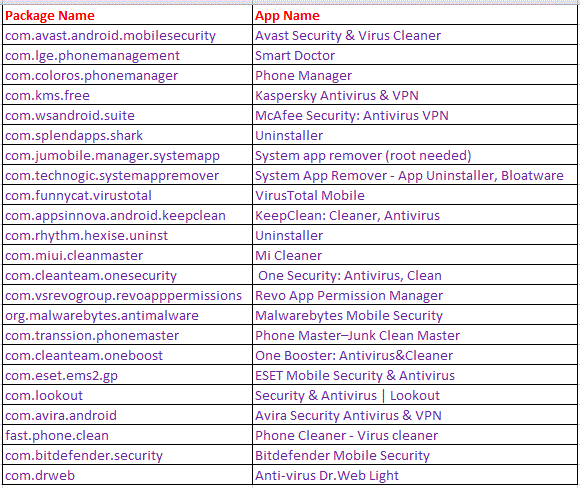
This malware also terminates a predefined list of apps’ process(es), as shown in Figure 12. Interestingly, that list includes a few popular security products as highlighted below, in order to remain undetected.
At K7, we protect all our customers from such threats. Do ensure that you protect your mobile devices with a reputable security product like K7 Mobile Security and scan your devices with it. Also keep your security product and devices updated and patched for the latest vulnerabilities to stay safe from such threats.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
| Package Name | Hash | K7 Detection Name |
| com.zynksoftware.docuscanapp | 13DF6443BF24D0E49566735B93F22646 | Trojan-Downloader ( 0058d95d1 ) |
| com.joy.slab | 04F4FB5E6CB95DFF7CCEE97B1F7D3636 | Trojan ( 0053b5f91 ) |
C2
hxxp://62[.]182[.]81[.]71/api/
hxxp://185[.]215[.]113[.]31:83/api








