Covid-19 pandemic has changed people’s behaviour significantly. Be it maintaining social distance, washing their hands more frequently, more of online shopping or panic buying; the approach has changed a lot. Nowadays, people have exponentially started relying on the digital world more than before. However, they do not seem to realise that some of their actions could make them victims of cyber attacks.
Our researchers at K7 Labs recently came across this twitter post
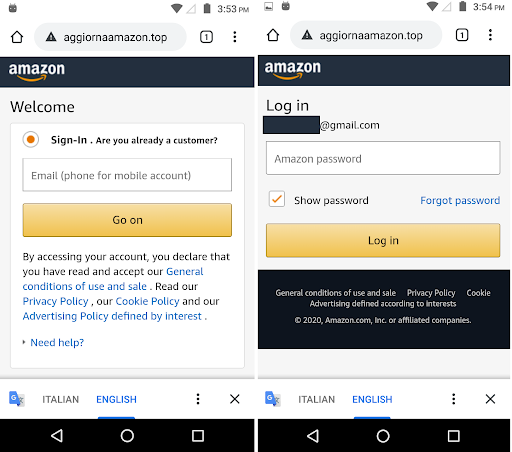
about a phishing campaign targeting Amazon Android users. This phishing page disguises as an online shopping portal to steal user’s credit card details. It is a variant of the Cerberus banking Trojan which has been blogged about earlier by our researcher. From this, we can figure that Cerberus is not only banking on using COVID-19 keywords to trick users, but is also taking advantage of changes in user’s behaviour to trap them.
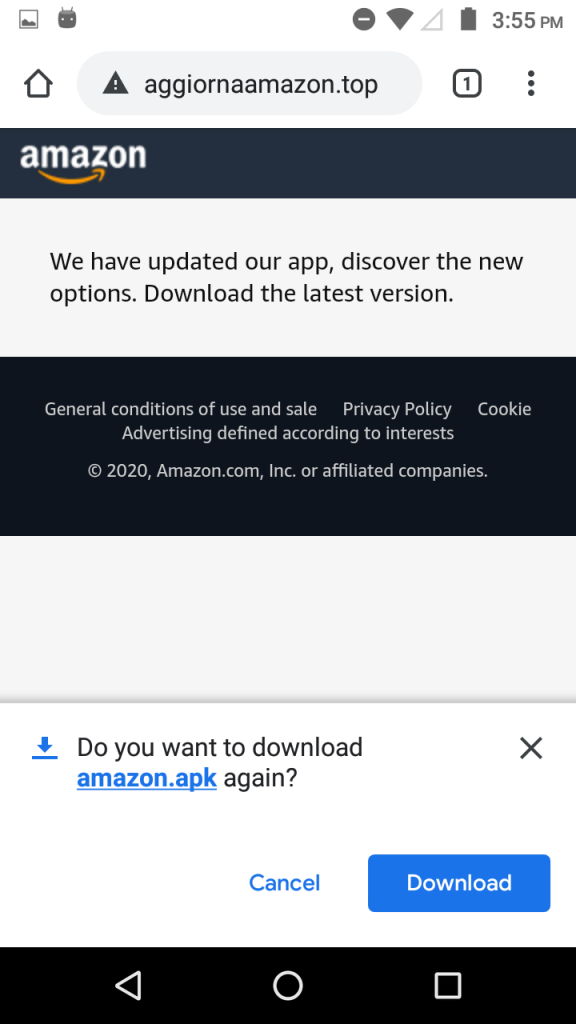
Victims are lured to visit the malicious link “http[:]//aggiornaamazon.top/amazon.apk” (one among many) and download the malware. Malicious behaviour of amazon.apk begins when the user downloads this app as shown in Figure 2.
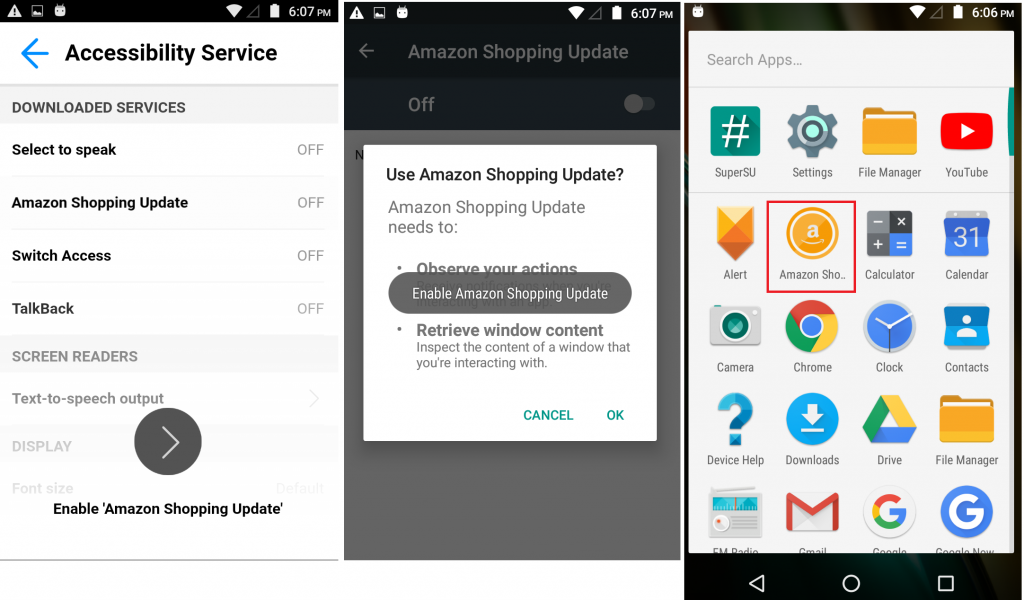
Once the installation is complete this Trojan prompts the user to enable accessibility service so that attackers can monitor user activities on the display screen as shown in Figure 3.
The Payload
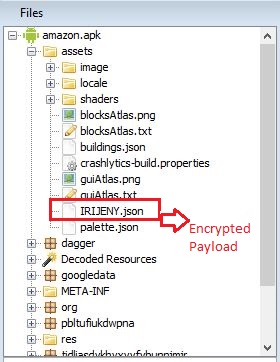
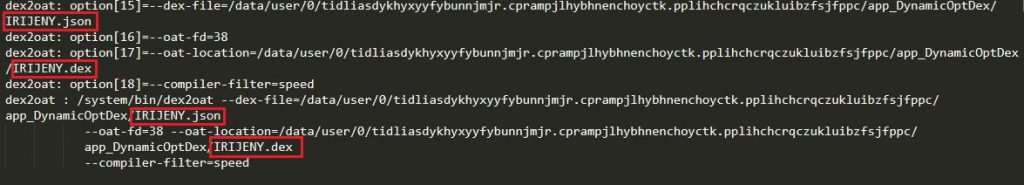
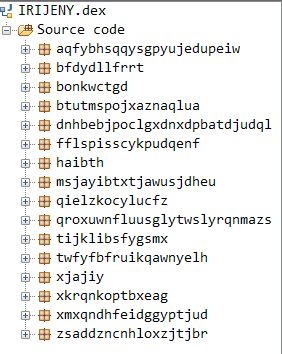
“amazon.apk” decrypts the malicious payload file called IRIJENY.json to an executable dex format, from the assets folder and loads the decrypted dex file as shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5 below. The logcat image shown in Figure 5 shows the IRIJENY.dex file execution at runtime.
When the payload IRIJENY.dex is decompiled it shows the obfuscated code of the malware as shown in Figure 6.
String Decryption
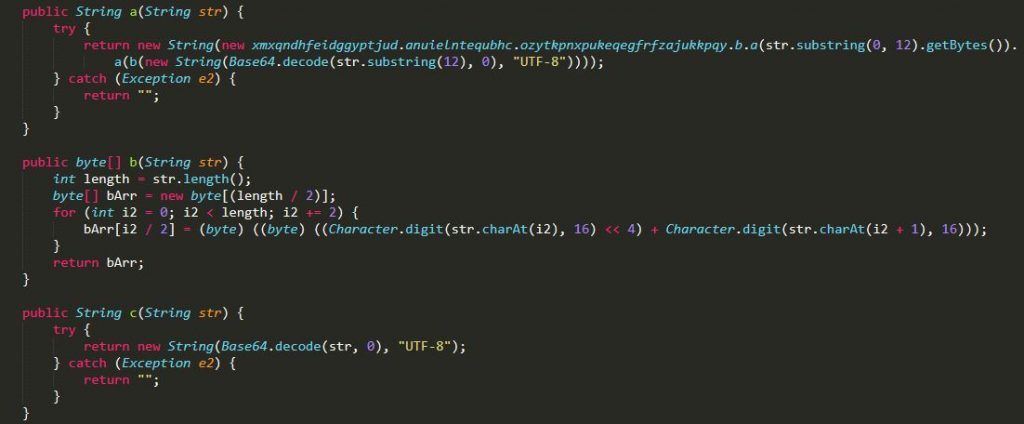
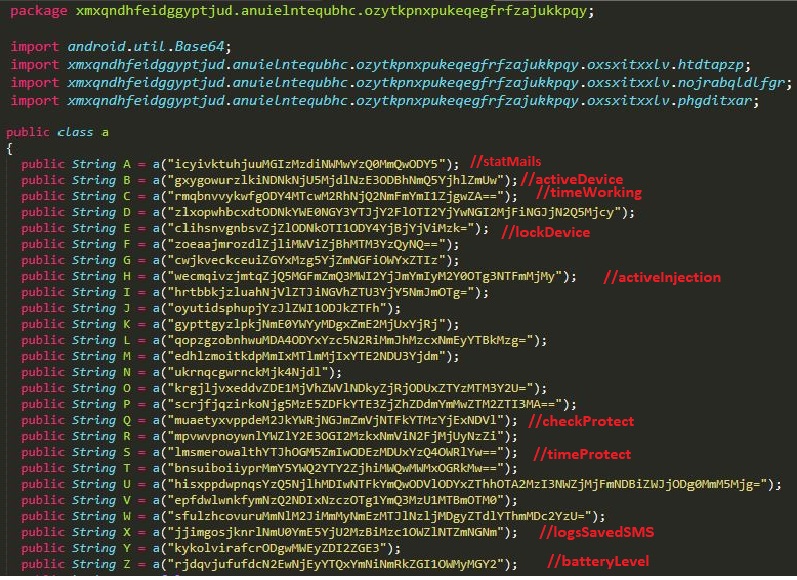
To evade detection, all the strings within the class, IRIJENY.dex are base64 encoded and the resulting decoded strings are RC4 encrypted strings with a decryption key specific to each string. Interestingly, each encrypted string has its unique RC4 decryption key prepended as the first 6 bytes of the encrypted string. Figure 7 shows the decoding and decryption routine used by the malware.
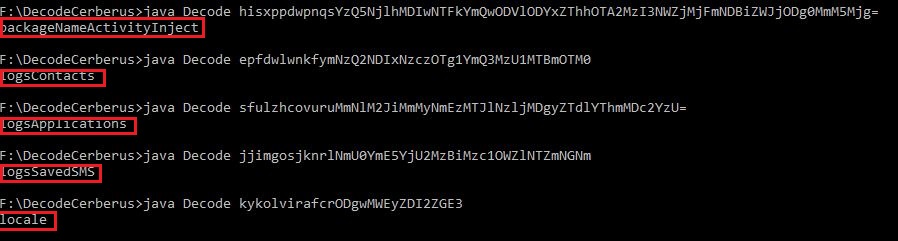
For instance, for the encoded string, “hisxppdwpnqsYzQ5NjlhMDIwNTFkYmQwODVlODYxZThhOTA2MzI3NWZjMjFmNDBiZWJjODg0MmM5Mjg=”, RC4 decryption key is “hisxppdwpnqs”, and the actual string is “packageNameActivityInject”.
The output after decrypting the strings for a few other encoded strings is as shown in Figure 8.
Figure 9 shows some of the decrypted strings (given in red) from the malware class file.
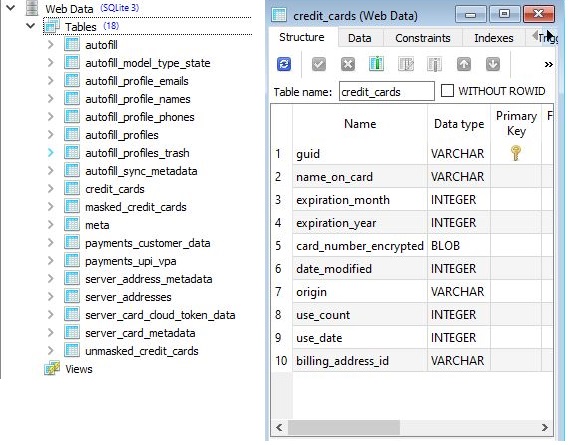
The goal of the Trojan is to exfiltrate detailed credit card data held on the device and store it to the SQLite database file called Web Data, created by the malware as shown in Figure 10.
C2 server communication
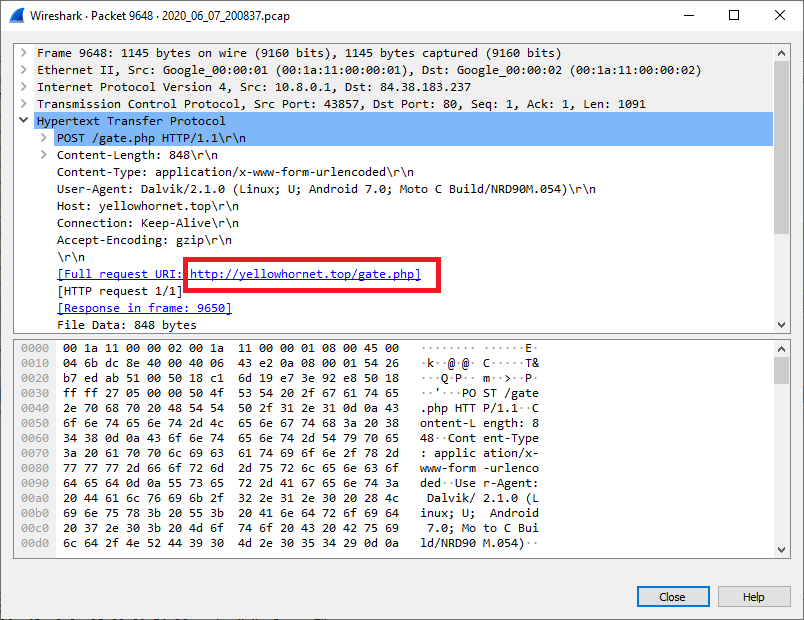
This malware then communicates to the C2 server “http[:]//yellowhornet.top” to transfer the exfiltrated data.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
Distribution: http[:]//aggiornaamazon.top/amazon.apk
C2: http[:]//yellowhornet.top
Hash: 2ce8a6a361ca57009cef9640c02dc44a3a084371c1f7a9d2ddc5b4d0394fd90a
K7 Detection Name: Trojan ( 005633ff1 )